Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water More than half the electricity in the United States comes from polluting coalfired power plants And power plants are the single largest source of heattrapping gas Fortunately, the use of alternative energy sources, such as solar, wind, geothermal, and hydro energy, is gaining increased support worldwideOne of several gases, especially carbon dioxide, that prevent heat from the earth escaping into space, causing the greenhouse effect We need a global system for limiting greenhouse gas emissions Radical steps to reduce greenhouse gases will have a huge effect on the economy

How Trump Is Ensuring That Greenhouse Gas Emissions Will Rise The New York Times
Greenhouse gasses definition
Greenhouse gasses definition-Greenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and Beyond slashing greenhouse gas emissions generated by people, the EU also wants to get better at drawing them down through natural




World Greenhouse Gas Levels Made Unprecedented Leap In 16
Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today farThe term "greenhouse gases," or GHGs, covers a wide variety of gases that, once they are released into the atmosphere, trap the sun's heat When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and trapped in the lower atmosphere, heating the EarthBefore we get to greenhouse gases, we need to cover the greenhouse effect This is when heat and energy from the sun get trapped in the Earth's atmosphere Some of this is a natural process, but gases created by human activity are trapping more heat in the atmosphere, raising the temperature and causing global warming or climate change These gases are therefore known as 'greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agentsOn , Colorado released its Greenhouse Gas Pollution Reduction Roadmap The Roadmap represents the most actionoriented, ambitious and substantive planning process that Colorado has ever undertaken on climate leadership, pollution reduction and The gas is also a significant contributor to climate change In 17, methane accounted for roughly 10 percent of all humandriven greenhouse gas emissions in the US, according to the EPA
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeWithdrawn Apr 5, 17; A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in




Greenhouse Gas Neutral Europe And The Role Of Geology Geoera




K1 Psx4w2wnatm
Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer A lot of the sun's energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back intoGreenhouse Gases Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases These include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases Solar radiation in the lower atmosphere acts like a "greenhouse" – thus the name – preventing heat from escaping Emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere is the main List Of Greenhouse Gases CO2 from fossil fuel consumption is the best known source of greenhouse gas, though certainly not the only one 11 Water Vapor (H2O) Water vapor, although it sounds innocent enough, is one of the biggest contributors to global climate change Interestingly, water vapor is not directly emitted from human activity



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News



Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate change is one of the most significant global challenges of the 21st century, posing major risks for developed and developing countries alike Despite our region's commitment to environmental protection, Bay Area residents generate greenhouse gas emissions at a rate substantially higher than the global averageNow, over a century later, the mention of greenhouse gas usually evokes thoughts of carbon dioxide (CO 2)That's mainly because changes in the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere have been linked to the warming of the atmosphere over this past century CO 2 is an important greenhouse gas, and along with water vapor, keeps the Earth warm enough to support life as we know it Greenhouse gas 4 Break out by 5 Year(s) * Percentages may not add to 100% due to independent rounding and the way the inventory quantifies US territories (not shown) as a separate sector Date range Note Values are rounded to the nearest hundredth Values of 000 may represent positive values less than 001 MMT CO2 Equivalent




How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut



Greenhouse Gas Emissions World Energy Data
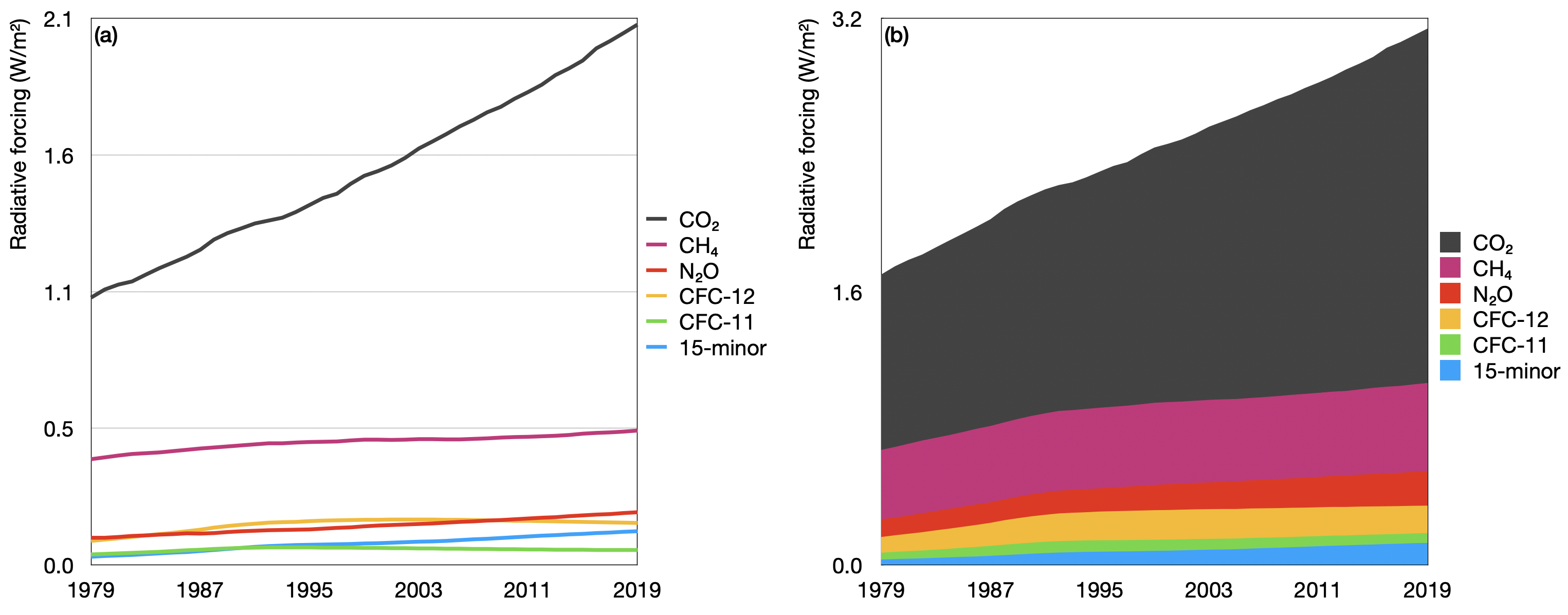
Global average abundances of the major, wellmixed, longlived greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, CFC12 and CFC11 from the NOAA global air sampling network since the beginning of 1979 These five gases account for about 96% of the direct radiative forcing by longlived greenhouse gases since 1750Greenhouse gas greenhouse gas Methane Methane (CH4) is the second most important greenhouse gas CH4 is more potent than CO2 because the radiative forcing produced per molecule is greater In addition, the infrared window is less saturated in the range of wavelengths of radiation absorbed by CH4, so more molecules may fill in the regionGreenhouse Gas submitters report as an emitter, a supplier, and/or a CO 2 injector Please select one of these types below Please select one of these types below By default emitters is selected



1



Greenhouse Gases
Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedGreenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are China's greenhouse gas emissions in 19 exceeded those of the US and the developed world combined, according to a report published Thursday by research and consulting firm Rhodium Group The




Removing Harmful Greenhouse Gases From The Air Using Energy From Plants Frontiers For Young Minds




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
After months of development and public meetings, we released a framework for the "Greenhouse Gas Assessment for Projects" rule, or "GAP rule," and is seeking to get feedback on that framework from local governments, businesses, tribal governments, associations, environmental groups, and other stakeholders before the agency releases a formal draft ruleUnder review Feb 19, 21, for revision and update) Notice of rescission of 19 draft guidance (Feb 19, 21) EO Protecting Public Health and the Environment and Restoring Science to Tackle theFinal guidance on consideration of greenhouse gas emissions and the effects of climate change (issued Aug 1, 16;



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons




France Greenhouse Gas Emissions Decreased By 16 9 From 1990 Levels Climate Scorecard
The NOAA Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI) measures the commitment society has already made to living in a changing climate It is based on the highest quality atmospheric observations from sites around the world Its uncertainty is very low The AGGI is analogous to the dial on an electric blanket Just as the dial does not tell you exactlyCarbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most important greenhouse gas, but not the only one – gases such as methane and nitrous oxide are also a driver of global warming Carbon dioxideequivalents (CO 2 eq) try to sum all of the warming impacts of the different greenhouse gases together in order to give a single measure of total greenhouse gas emissionsThe distribution of atmospheric water vapor, a significant greenhouse gas, varies across the globe During the summer and fall of 05, this visualization shows that most vapor collects at tropical latitudes, particularly over south Asia, where monsoon thunderstorms swept the gas some 2




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Nh Department Of Environmental Services




Nahb Residential Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from electricity have increased by about 12 percent since 1990 as electricity demand has grown and fossil fuels have remained the dominant source for generation To learn about projected greenhouse gas emissions to , visit the US Climate Action Report 14 (310 pp, 23 M, About PDF)Some of the greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, ozone, water vapor and a few others The process of creating electricity, running cars, using landfills and making chemicals are some of the top ways we are releasing more and more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere NOAA index tracks how greenhouse gas pollution amplified global warming in Extra heat trapped in the atmosphere by humancaused greenhouse gas pollution continued to exacerbate global warming in , driven by historically high emission levels that were largely unaffected by the economic slowdown stemming from the pandemic, NOAA scientists reported




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human made Human activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere over the last 150 years 1 The largest source of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities in the United States is from burning fossil fuels forGreenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as light




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Rggi
Much like the glass of a greenhouse, gases in Earth's atmosphere sustain life by trapping the sun's heat These "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the makeup of our atmosphere Earth is sometimes called the "Goldilocks" planet – it's not too hot, not too cold, and the conditions are just right to allow life, including us, to flourishAny of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation
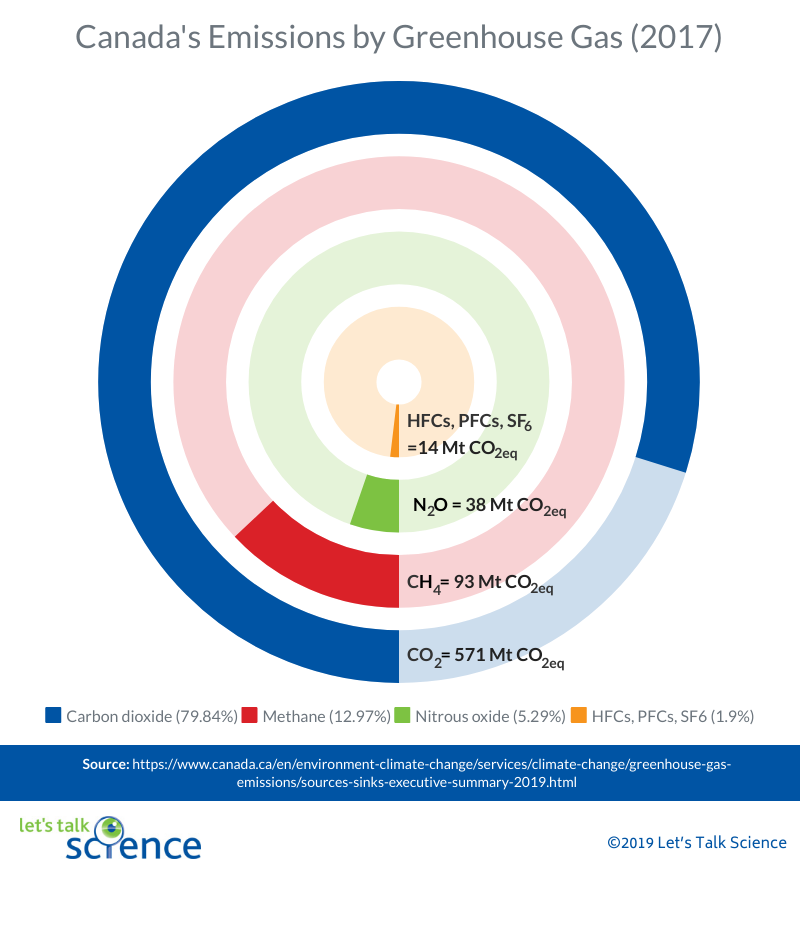



What Are Greenhouse Gases Let S Talk Science




World Greenhouse Gas Levels Made Unprecedented Leap In 16
Greenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil and natural gasThe largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and RussiaYou are About to View Greenhouse Gas Quantities from Suppliers Important Information about this Data Set Suppliers are facilities or entities that supply certains products (eg, fossil fuels or industrial gases) into the economy that, when combusted, released, or What are greenhouse gases?
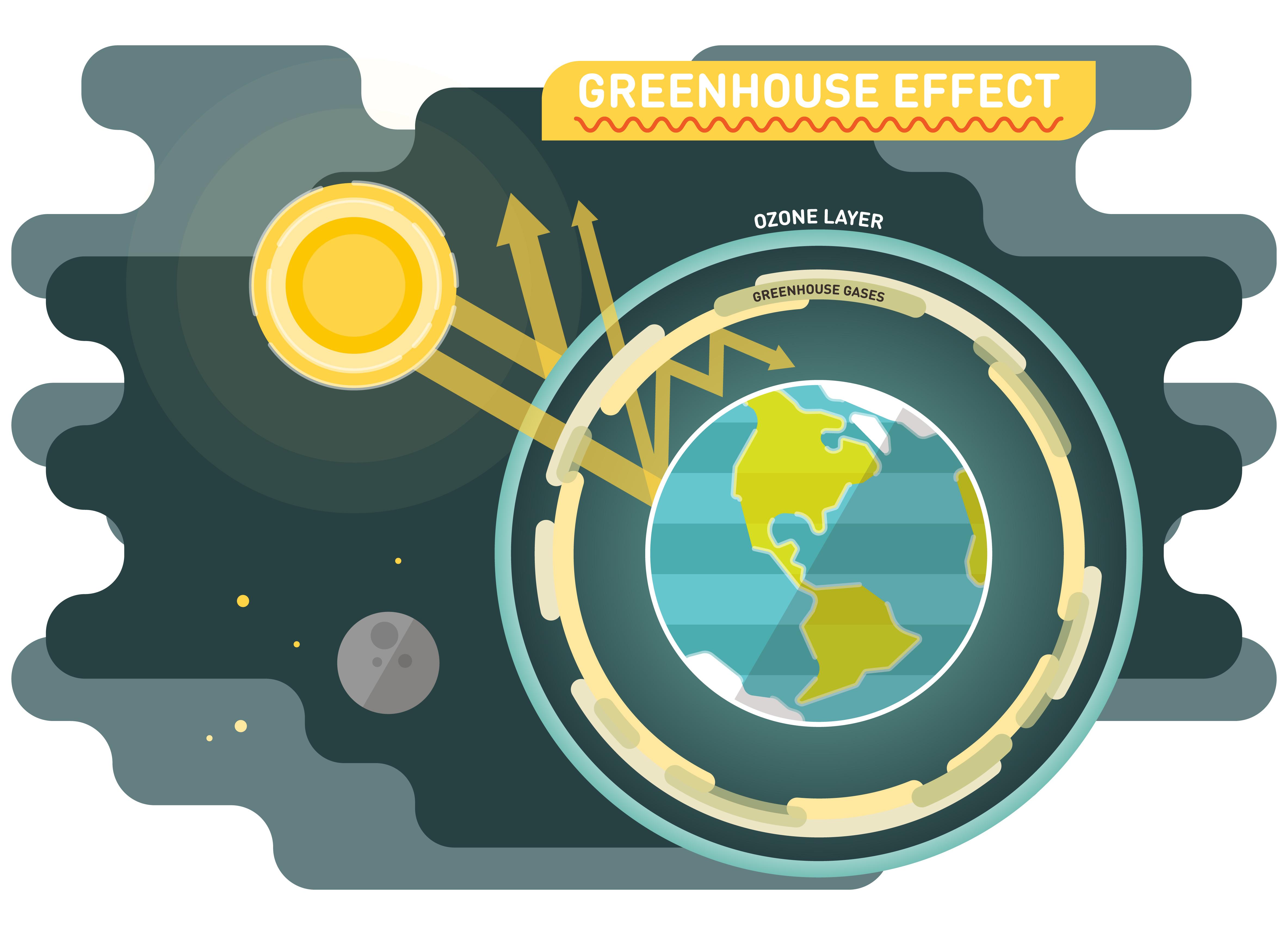



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate




Why We Measure Track Ghgs Sustainable Practices The Office Of Sustainability Umass Lowell
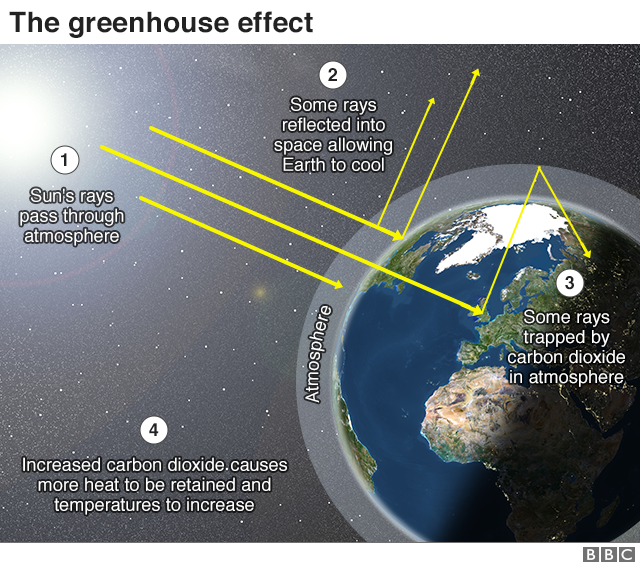
Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does notTo stop climate change, we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasingFor the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing we can stop The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight
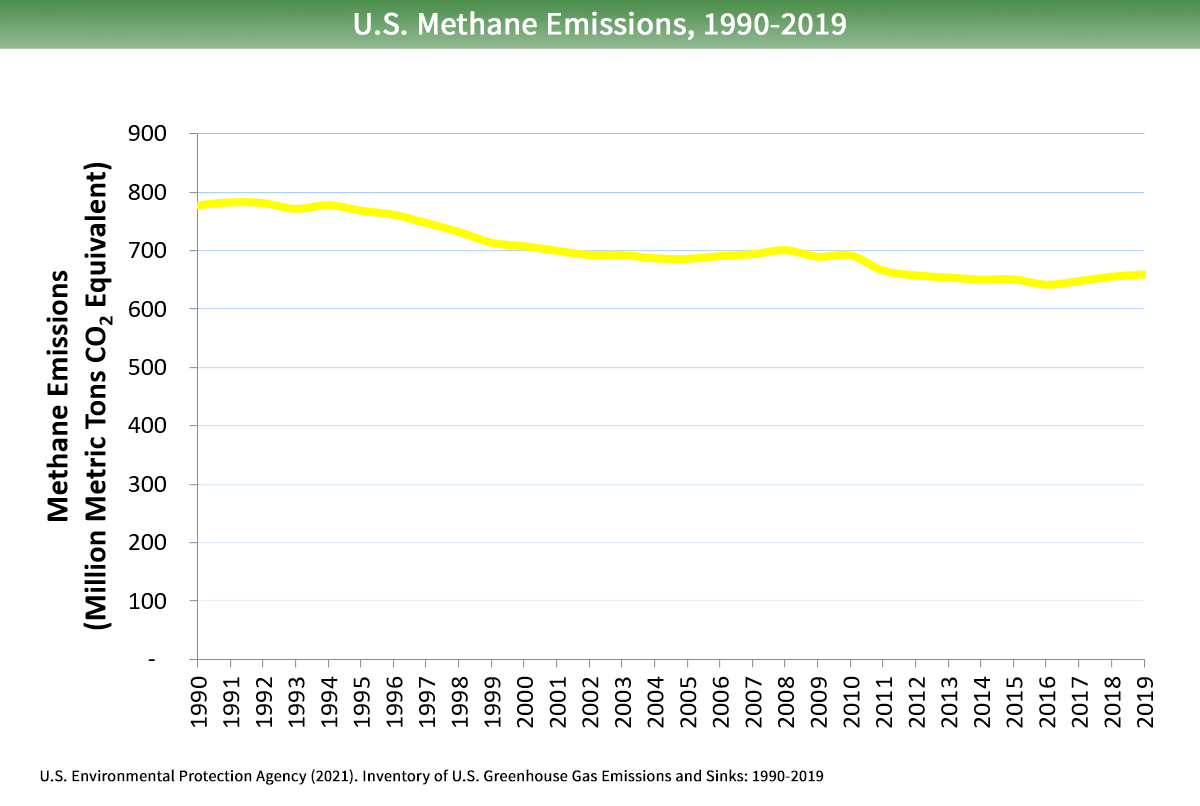



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases World Meteorological Organization
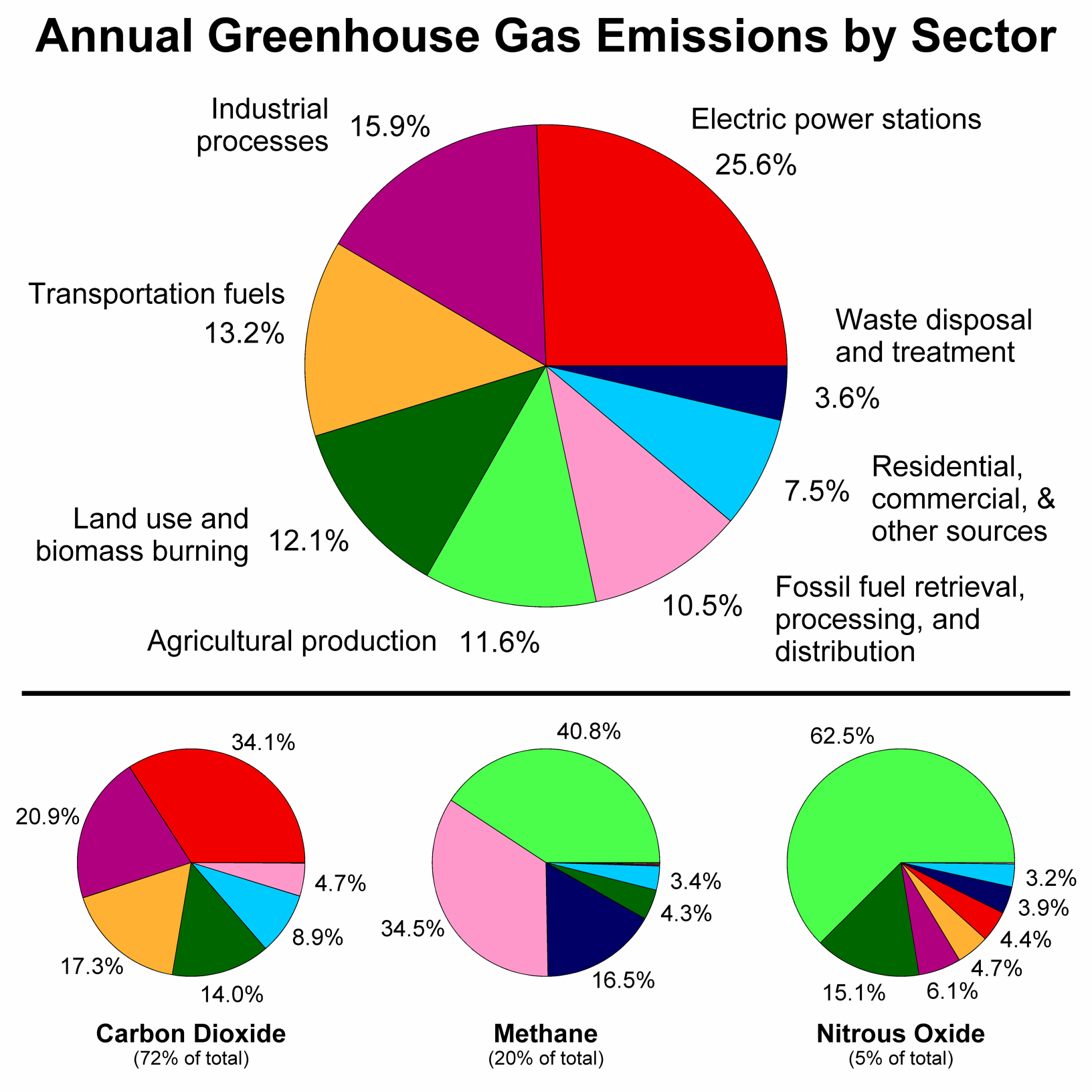
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Limiting Future Impacts of Climate Change Sources of Greenhouse Gases (GHG) in New York Efforts over the past decade to reduce emissions from the power sector have made New York's electricity some of the cleanest in the nation, and now transportation is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in New YorkMethane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphere A chemical used in the creation of semiconductors, hexafluoroethane is the Methuselah of greenhouse gases While some chemicals linger in the atmosphere for mere decades, hexafluoroethane sticks



Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Two Degree Difference Us Greenhouse Gas Emissions Down 10 In



Progress To Greenhouse Gas Emission Targets European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Hiding Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The Cloud Nature Climate Change




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record World Meteorological Organization




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know




Greenhouse Gases What Is Warming Up Our Earth
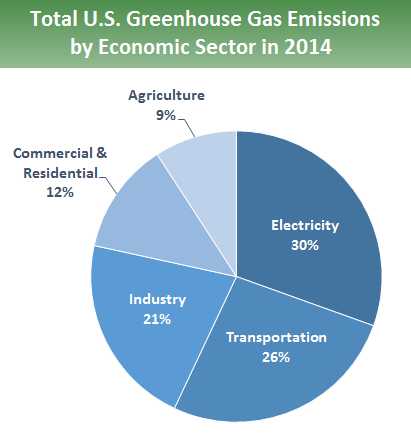



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Banning The Super Greenhouse Gas Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 17 10 16




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
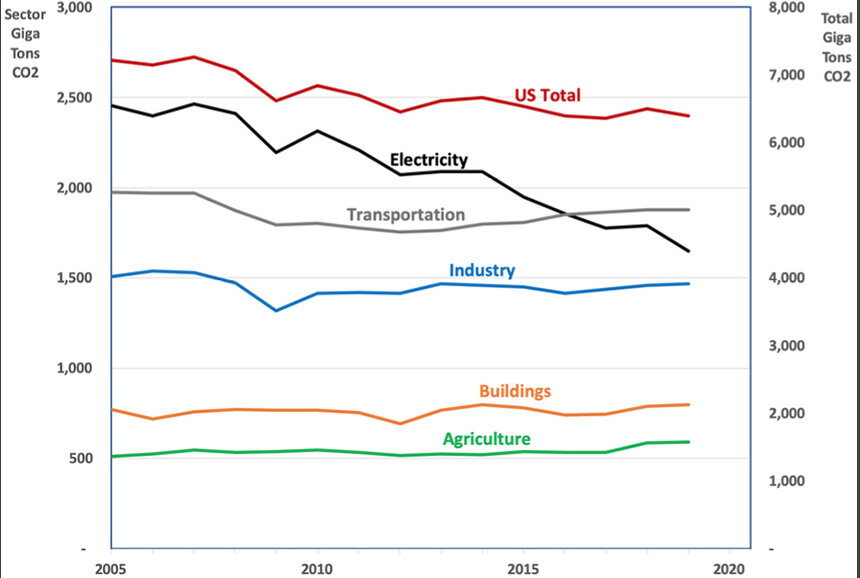



No Progress Made To Reduce U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ecori News




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Japan To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions To Net Zero By 50 Nikkei Asia



Chart China Beats U S Europe In Combined Greenhouse Gases Statista




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




They Just Kept On Rising Data Reveals Alarming Greenhouse Gas Increase




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Matt Canavan Shrugs Off Australia S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Increase Energy The Guardian




Greenhouse Gases 101 Ben Jerry S
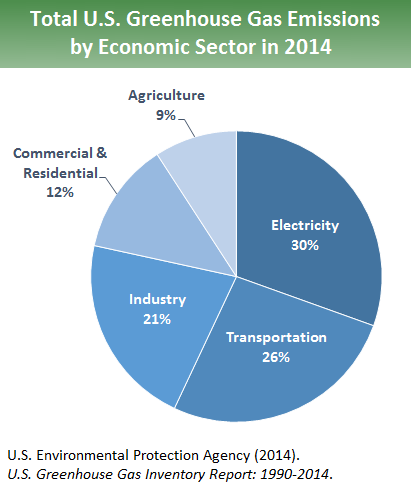



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Pork Production And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pork Information Gateway




How Trump Is Ensuring That Greenhouse Gas Emissions Will Rise The New York Times
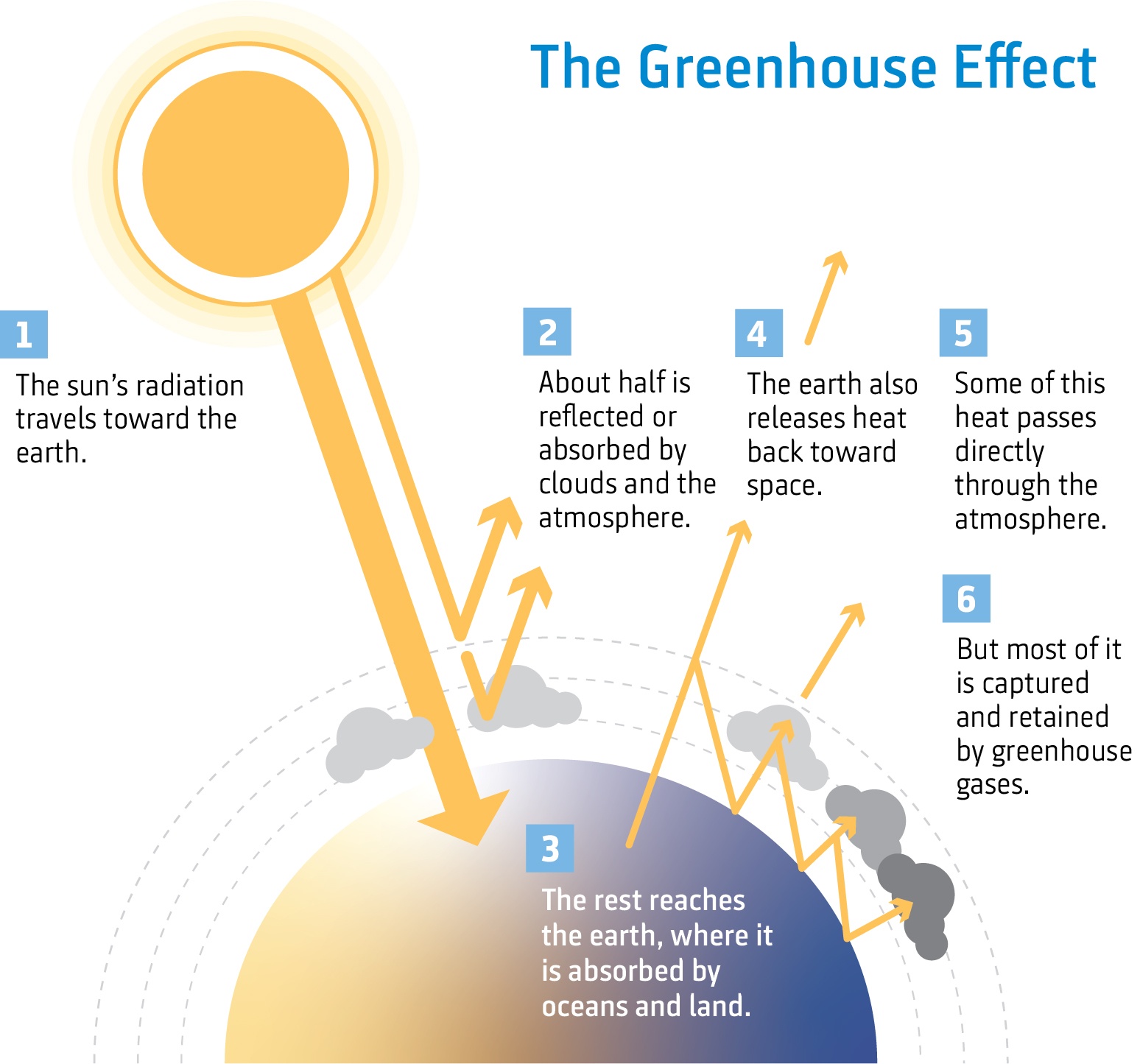



Climate Change The Science Niwa



1




Human Activity Caused The Long Term Growth Of Greenhouse Gas Methane




What Does The Spike In U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Mean




N Jwv Utax0edm



Small Increase In Eu S Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 17 With Transport Emissions Up For The Fourth Consecutive Year European Environment Agency




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
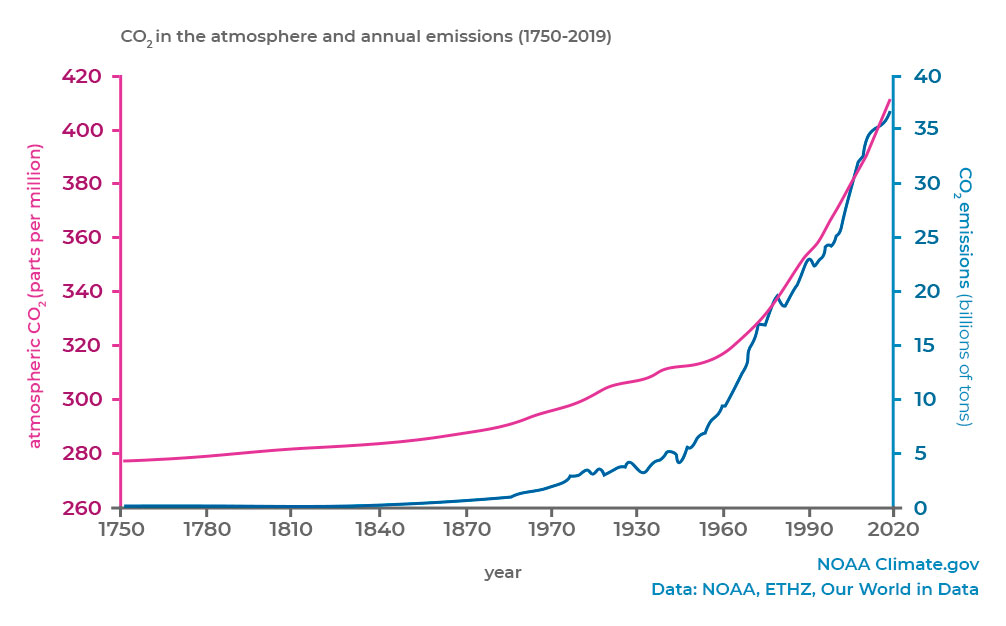



Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Proterra Foundation




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




Automating Greenhouse Gas Measurements
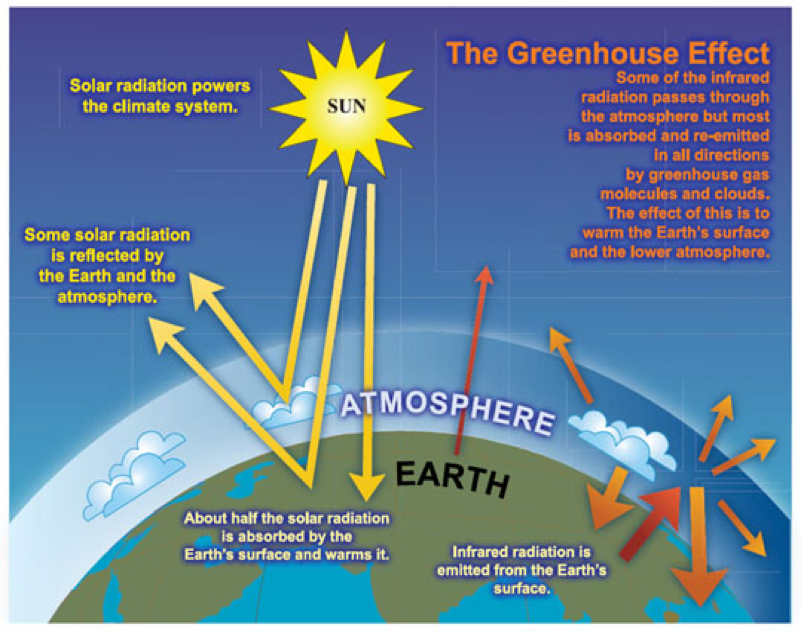



Greenhouse Gas Reduction




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




What Is The Greenhouse Effect The Environment For Kids Updated Version Youtube




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
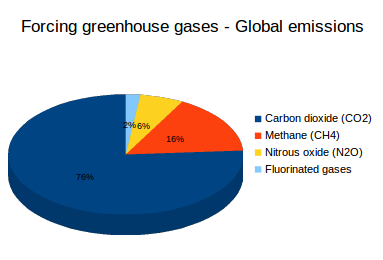



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact
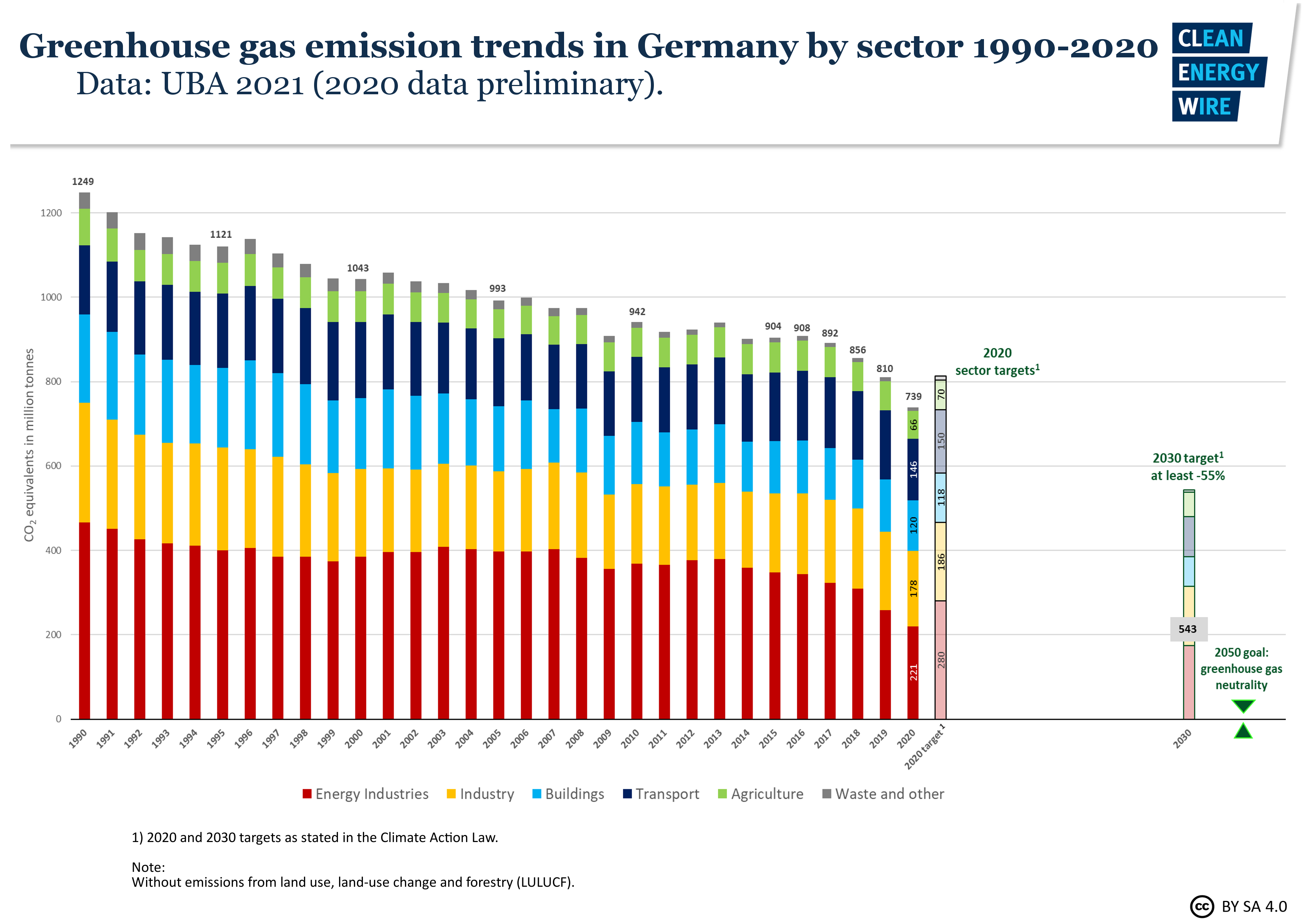



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
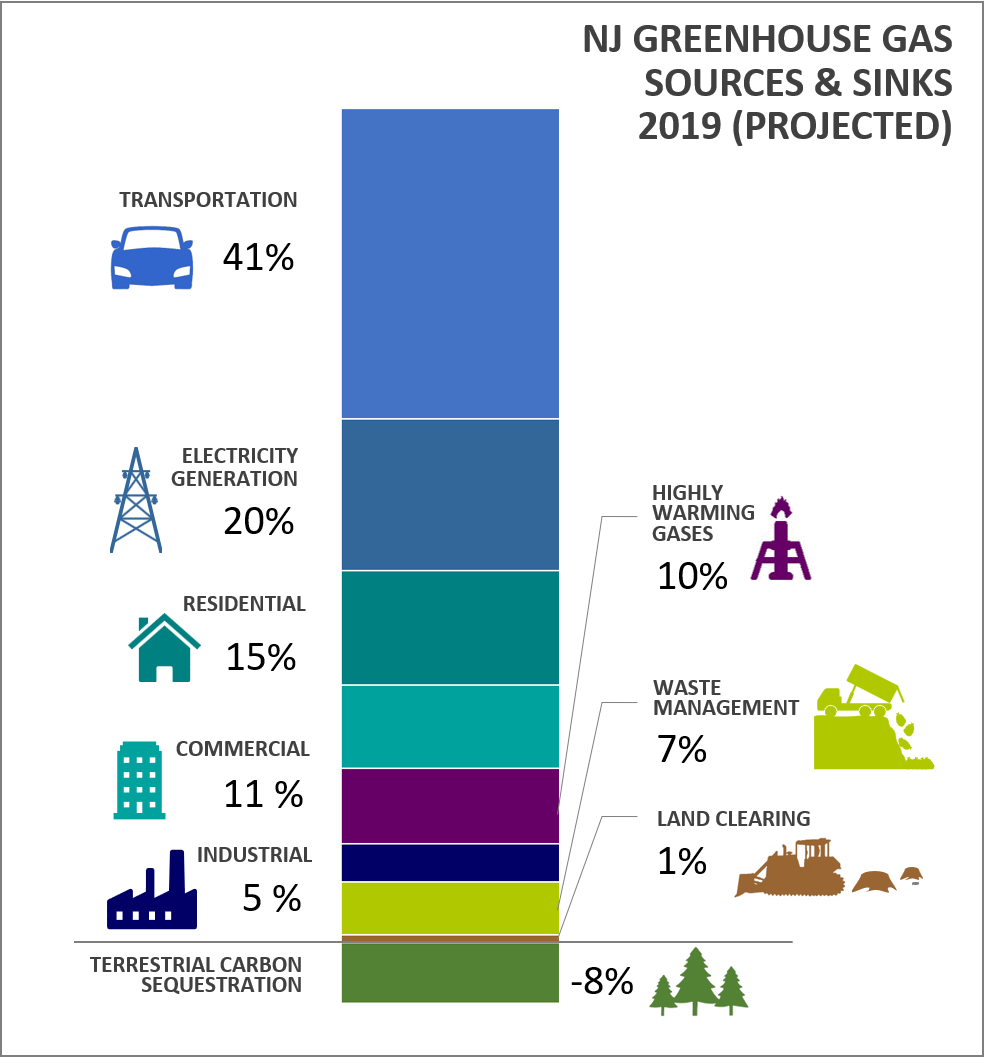



Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
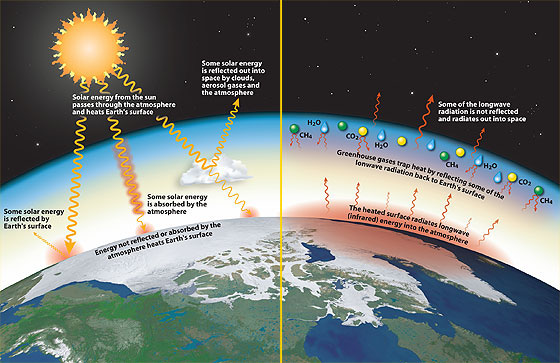



Too Much Of A Good Thing



Q Tbn And9gcqx8qqb7vyjubela12bb Jefr3jui9po9norhhsaq Qhlnrfuaa Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
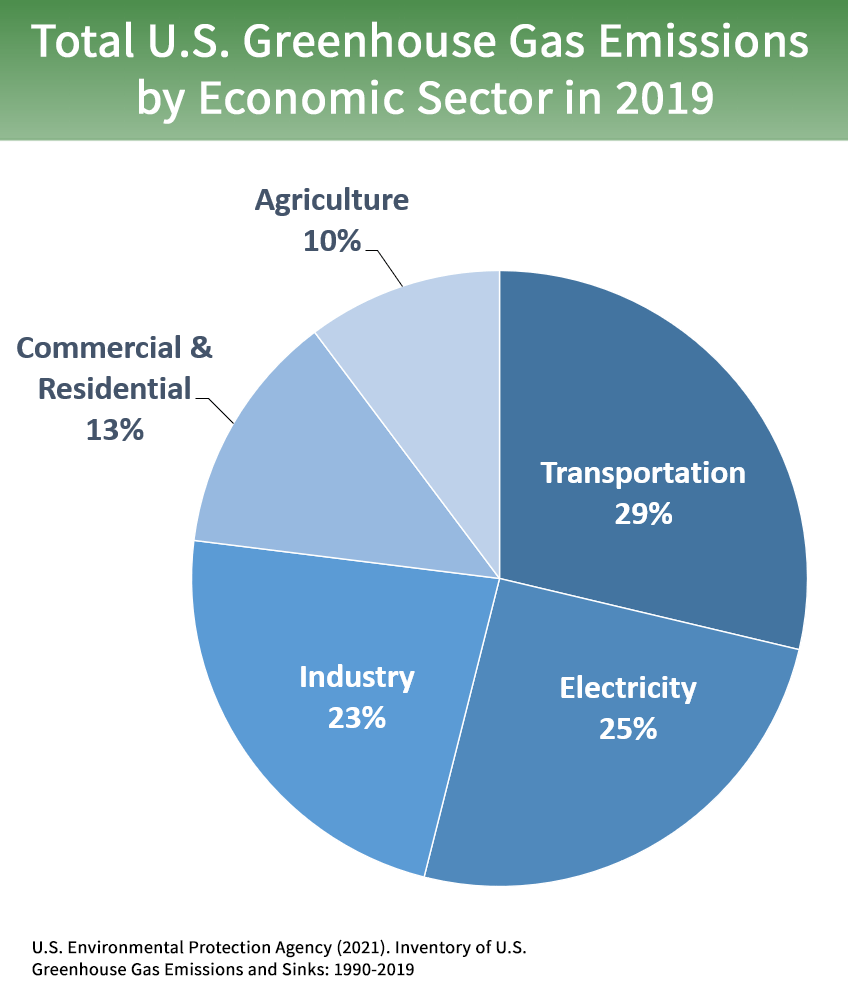



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist
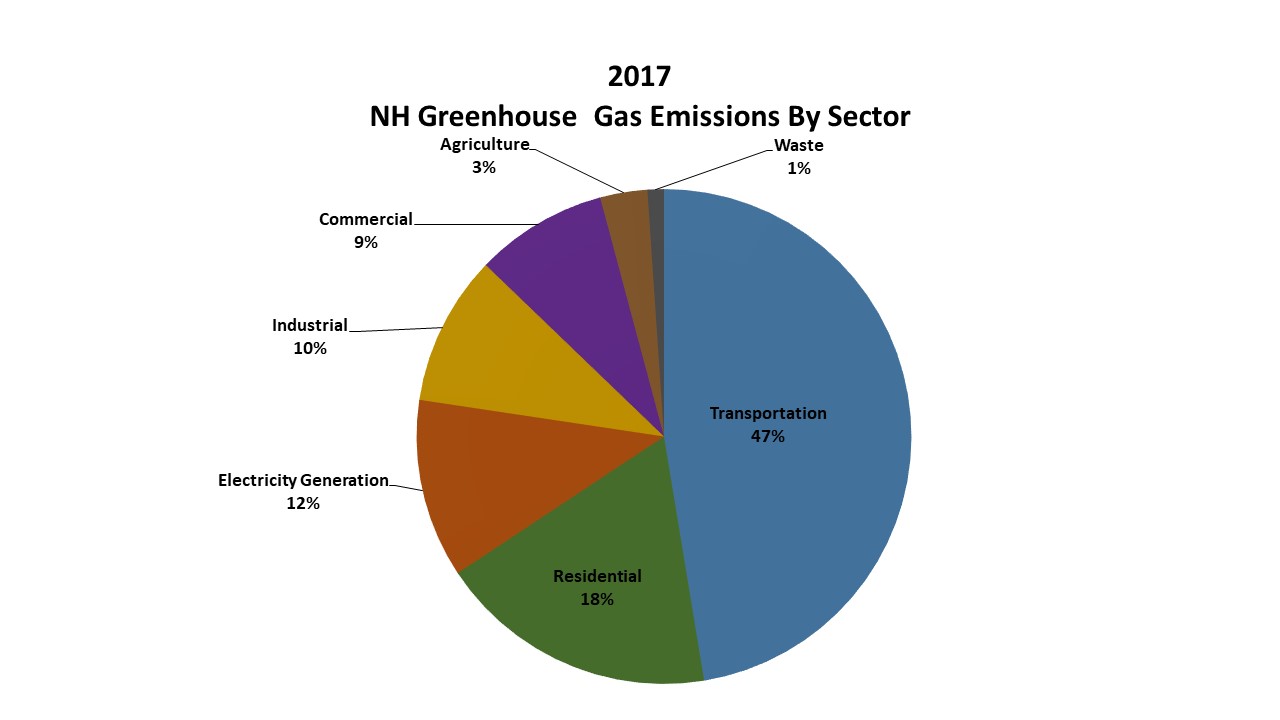



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Nh Department Of Environmental Services



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
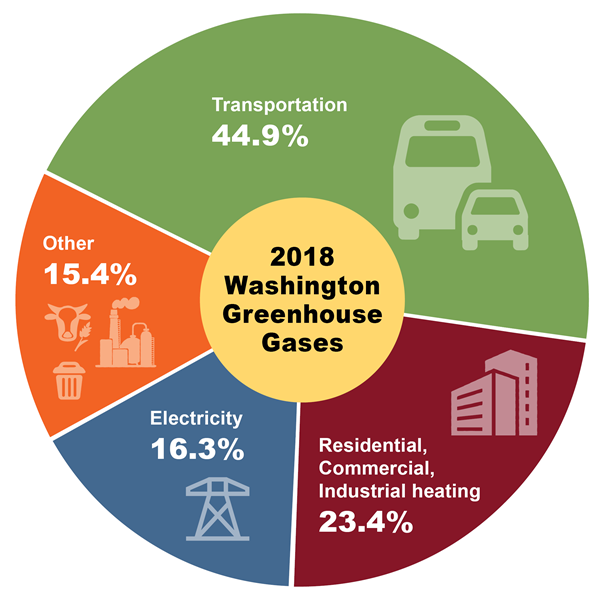



18 Data Washington State Department Of Ecology




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases The Australian Museum
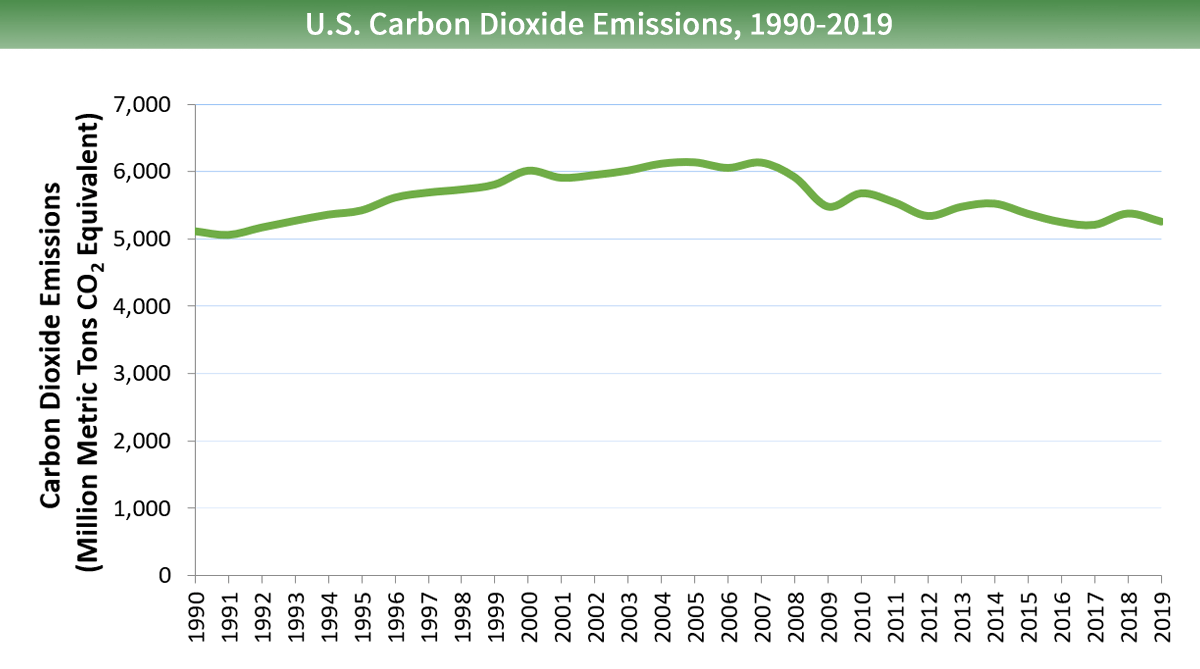



K1 Psx4w2wnatm




Saudi Arabia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Have Increased By 225 Since 1990 Climate Scorecard




Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Inventory Partner Energy
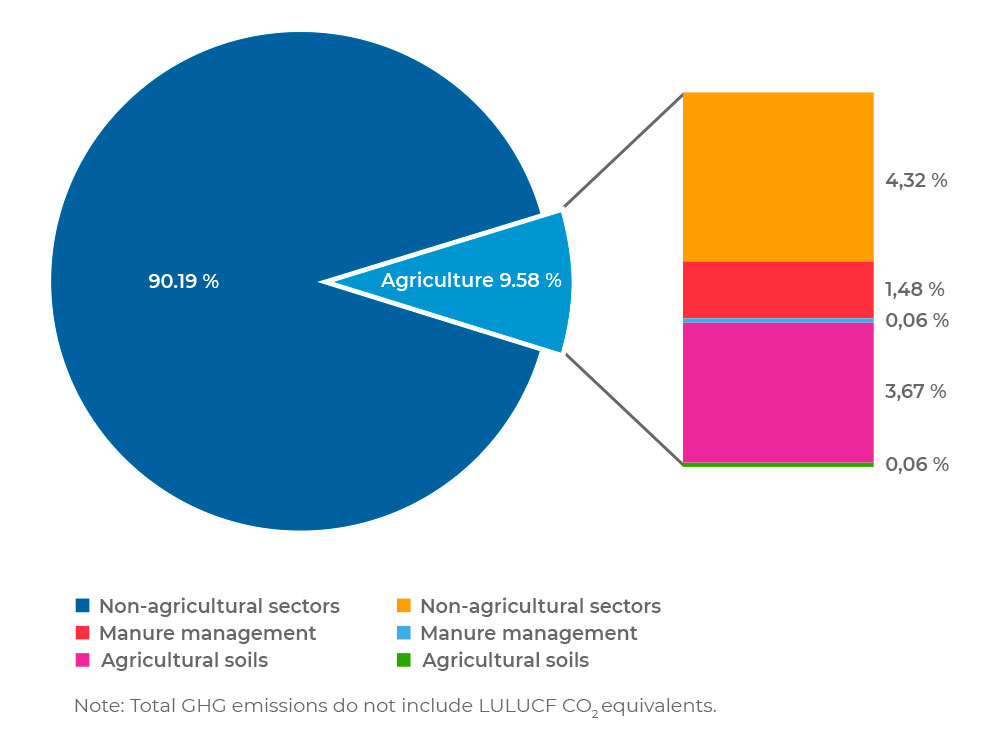



Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Proterra Foundation
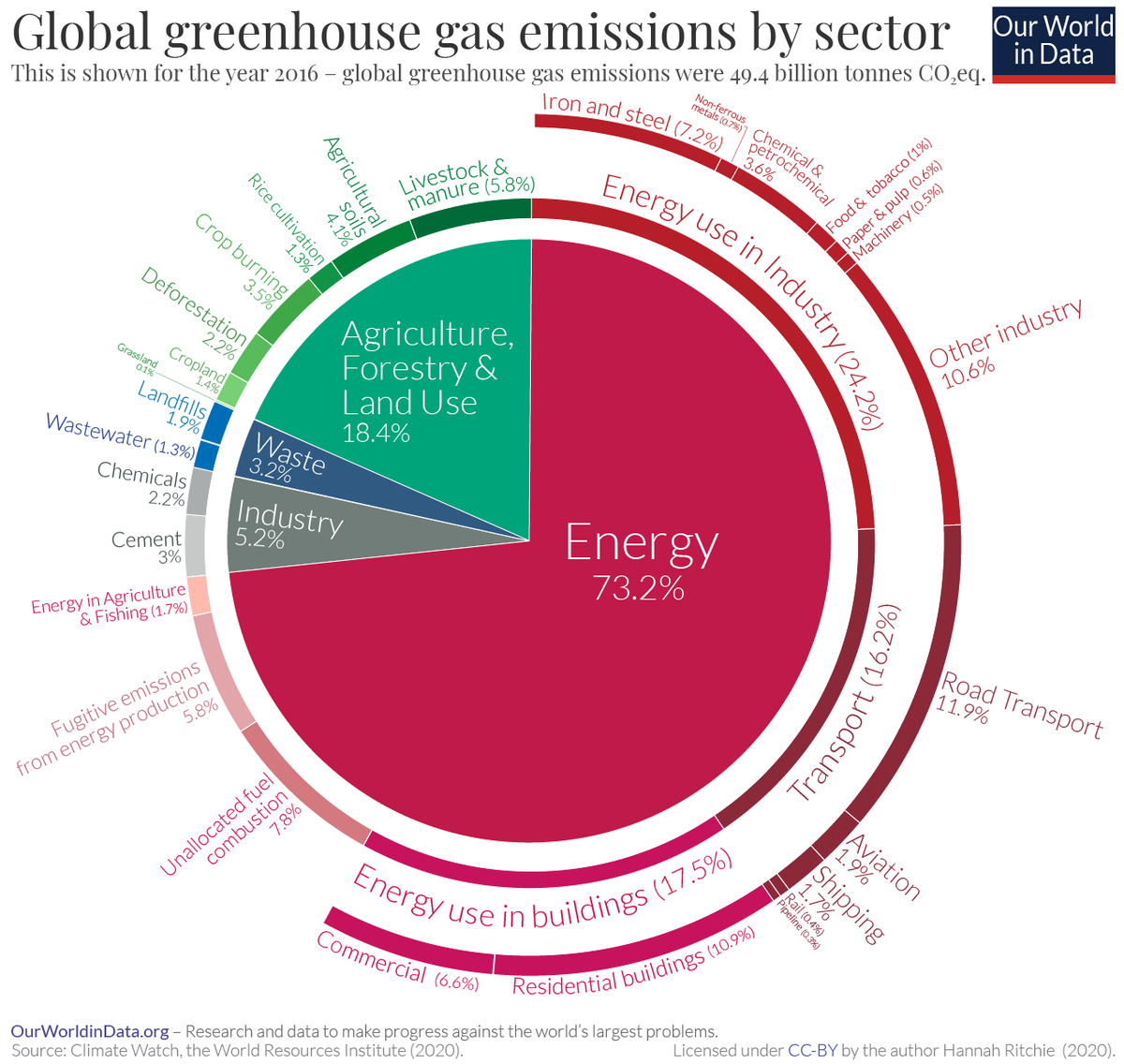



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Uk Fell 3 In 18 Official Figures Show Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Guardian




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunge In Response To Coronavirus Pandemic Inside Climate News




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Santa Fe City Of Santa Fe New Mexico




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 18 Source Epa 15 Overview Of Download Scientific Diagram



Q Tbn And9gctaj8wii876qu Vg Qiwf0vbxzn5m2dj2uyfahncczk01qi3 Z7 Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Grain How Much Of World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Agriculture




Why We Measure Track Ghgs Sustainable Practices The Office Of Sustainability Umass Lowell
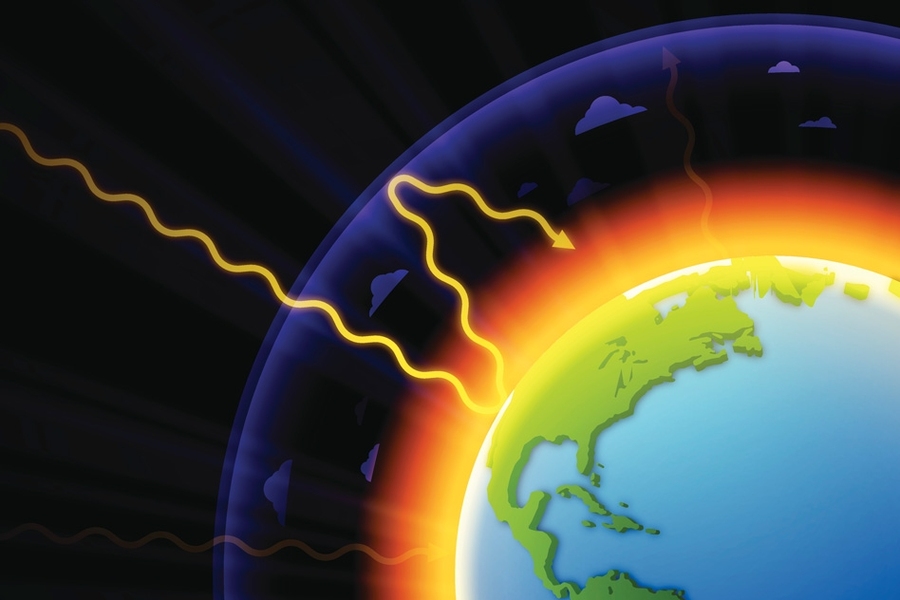




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
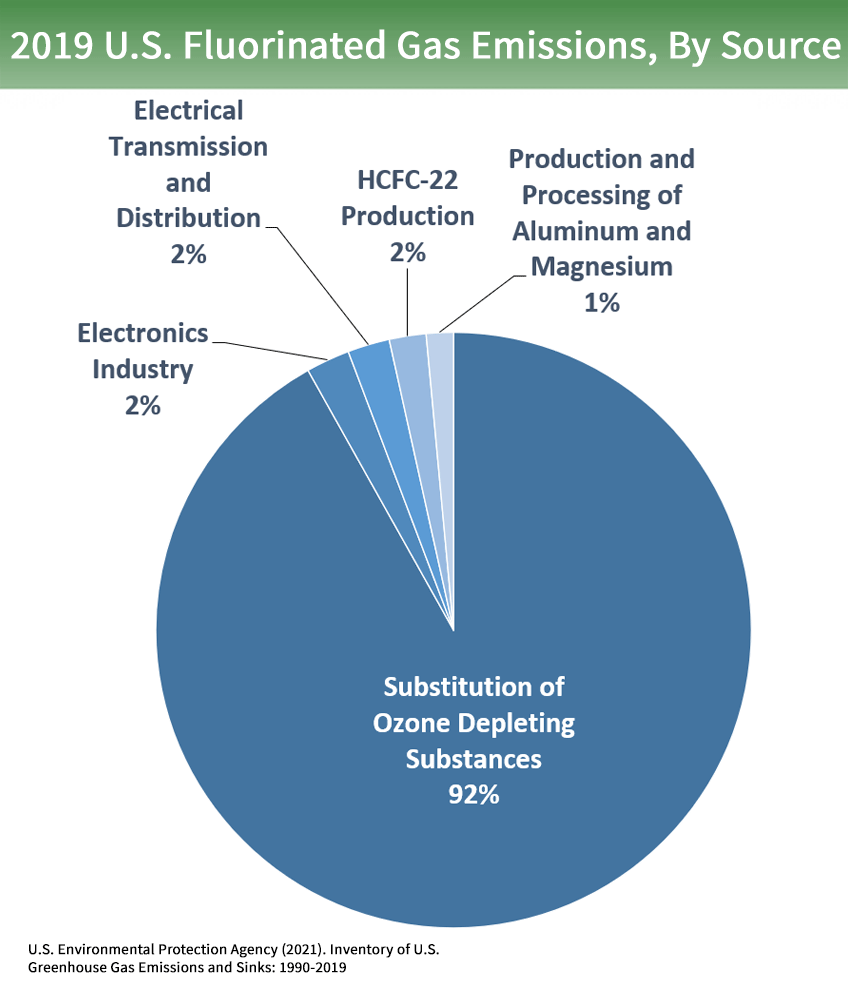



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿