What is the greenhouse effect and which gases are important?Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution, coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphere For example, water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, but carbon dioxide has a more significant impact on global warming due to its abundance in the atmosphere plus its relatively long

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
How does the greenhouse gas effect work
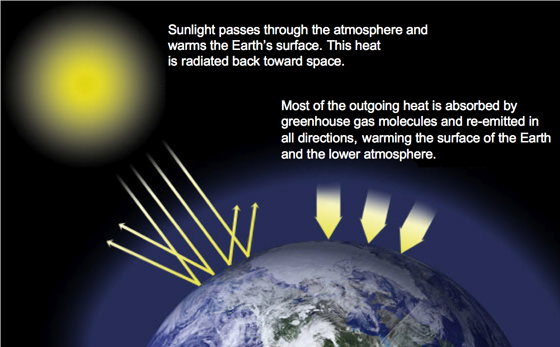
How does the greenhouse gas effect work- Greenhouse gases trap heat that would otherwise escape into space and they radiate it back towards the earth's surface a phenomenon known as the 'greenhouse effect' The growth of greenhouse gas emissions may be linked to rising temperatures, otherwise referred to asEnergy from sunlight is also the source of the warmth on Earth, because the atmosphere is pretty transparent to sunlight However, the way the Earth and its atmosphere work to stay warm is different from the way a greenhouse works, so the term "greenhouse effect" is a bit misleading A different analogy is the atmosphere acting like a blanket




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube
The natural warming influence of greenhouse gases—the greenhouse effect—keeps Earth's temperature friendly to life; The Greenhouse Gas Effect The greenhouse effect is a natural process by which some of the radiant heat from the Sun is captured in the lower atmosphere of the Earth, thus maintaining the temperature of the Earth's surface The gases that help capture the heat, called ?greenhouse gases,? The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface
N 2 O or Nitrous Oxide is a greenhouse gas NO and NO 2 (nitric oxide or nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide) emissions cause global cooling through the formation of (OH) radicals that destroy methane molecules, countering the effect of GHGs Carbon Monoxide Carbon monoxide is a shortlived greenhouse gas (it is less dense than air)Total US Emissions in 19 = 6,558 Million Metric Tons of CO 2 equivalent (excludes land sector) Percentages may not add up to 100% due to independent rounding Larger image to save or print Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gasesUp until about 150 years ago, human activity did not produce many greenhouse gases That changed as forests were cleared to make way for cities and farms, and as important inventions and industrial innovations, like the widespread use of
The greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would beInclude water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrousThe Greenhouse Effect Explained Source National Park Service Where do greenhouse gases come from?




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
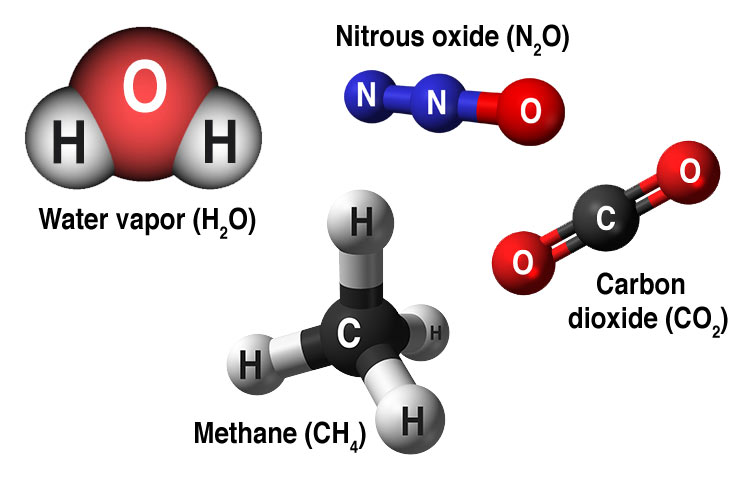
Without greenhouse gases, the planet's average temperature would be below freezingThe Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming How the Greenhouse Effect Works Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an atmospheric constituent that plays several vital roles in the environment It absorbs infrared radiation in the atmosphere It plays a crucial role in the weathering of rocks Greenhouse Gas Induced Global Warming The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and fluorinated gases




Primary Environment The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT this observed temperature rise can be explained by increases in greenhouse gases The same models predict a further 15 K temperature rise over the next century as greenhouse gases continue to increase If X is a greenhouse gas, then adding Dm will decrease the outgoing terrestrial flux at the top of the And water vapour is a greenhouse gas as we all know very well If the earth's atmosphere cools so the water vapour drops AMPLIFYING the primary cooling effect Amplification is exactly what water vapour does with respect to thermal effects on atmospheric temperature It's exactly the right term to useThe most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), and methane When there is more greenhouse gas in the air, the air holds more heat This is why more greenhouse gases cause climate change and global warming The greenhouse effect is natural




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Primary Environment The Greenhouse Effect Explained
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides As explained before, the greenhouse effect acts like insulation Think of a house in winter If you've got a heating system (the Sun) but no insulation (greenhouse gases) then the heat escapes quickly and the house (planet Earth) stays cold Water vapor The most abundant greenhouse gas, but importantly, it acts as a feedback to the climate Water vapor increases as the Earth's atmosphere warms, but so does the possibility of clouds and precipitation, making these some of the most important feedback mechanisms to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide (CO 2 )




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau
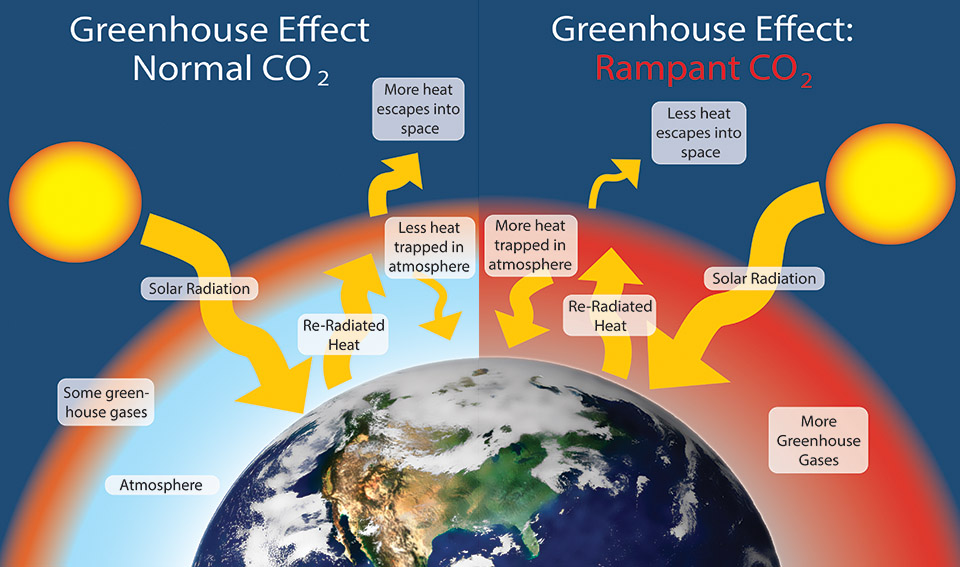
Unusual Arctic warming explained by overlooked greenhouse gases By Rodrigo Pérez Ortega Jan 21, , 430 PM The same gases that caused holes in Earth's ozone layer in the past century are If the atmosphere works too well as a greenhouse, each day gets a little warmer and a little warmer We may not be able to measure this effect from day to day or even year to year But over tens of years, a few degrees of warming starts causing changes For example, ice melts in the North and South Pole regions Today, the numbertwo producer of humancaused greenhouse effects is methane, the main constituent of natural gas When initially released, methane is about 100 times more potent than carbon dioxide, but its lifetime in the atmosphere is much shorter — about a decade, unlike carbon dioxide's residence time of centuries




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet



How Do Greenhouse Gases Trap Heat Socratic
How are manmade greenhouse gas emissions changing the Earth's atmosphere, and what needs to hap The Main Greenhouse Gasses The most important GHGs directly emitted by humans include CO 2 and methane Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas that is contributing to recent global climate changeCO 2 is a natural component of the carbon cycle, involved in such activities as photosynthesis, respiration, volcanic eruptions, and oceanHow the greenhouse effect works It's thought that the buildup of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways The gases allow more of the sun's rays to enter the atmosphere
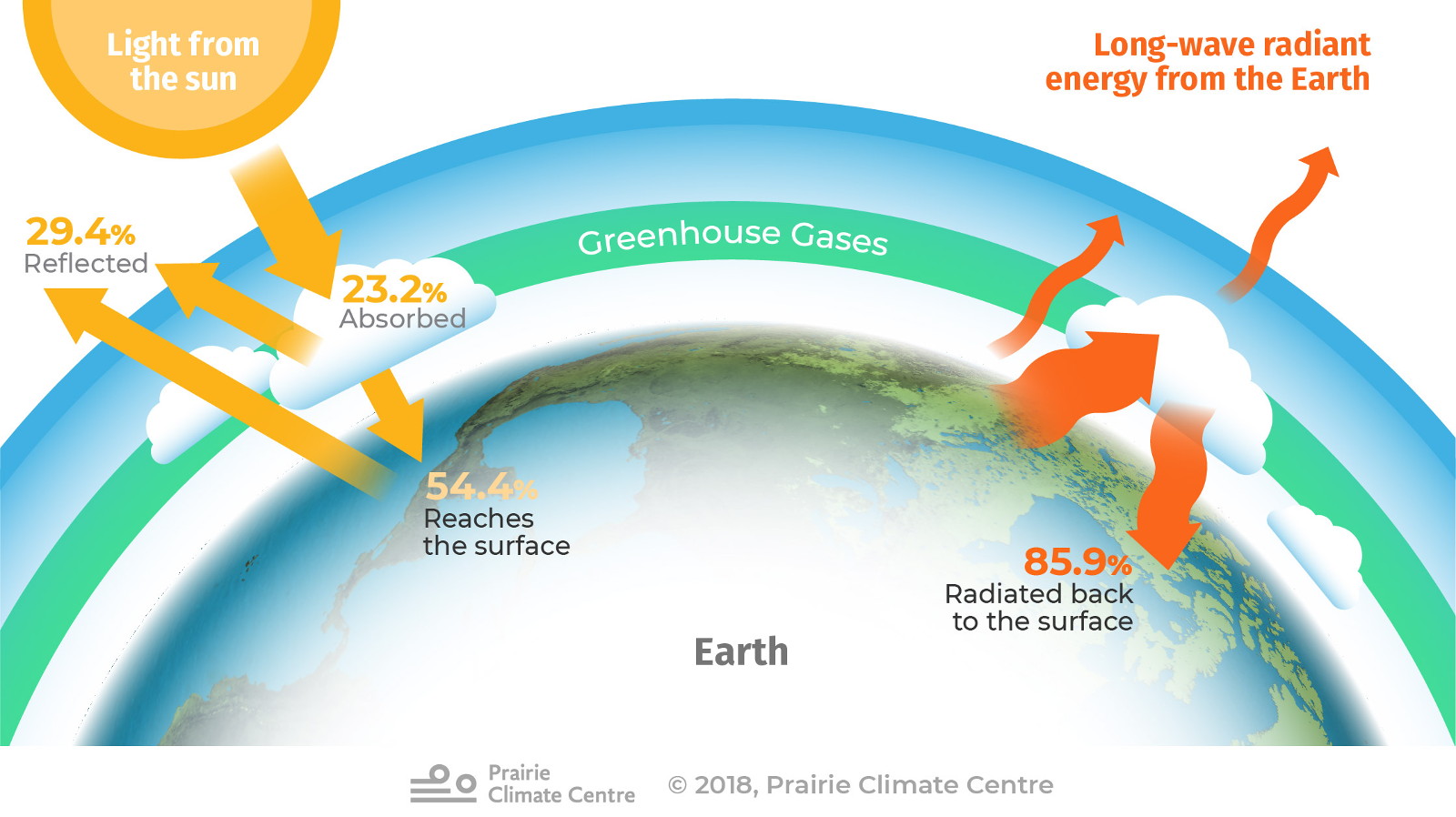



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada



Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
For thousands of years, the global greenhouse gas supply was essentially stable Natural processes removed as much carbon from the atmosphere as they released Human activities like burning fossil fuels have added huge quantities of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide to our atmosphere, creating a "greenhouse effect" that traps energy Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most important greenhouse gas, but not the only one – gases such as methane and nitrous oxide are also a driver of global warming Carbon dioxideequivalents (CO 2 eq) try to sum all of the warming impacts of the different greenhouse gases together in order to give a single measure of total greenhouse gas The most abundant greenhouse gas in Earth's atmosphere is water vapour and it is this gas that provides the natural greenhouse effect Without this




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
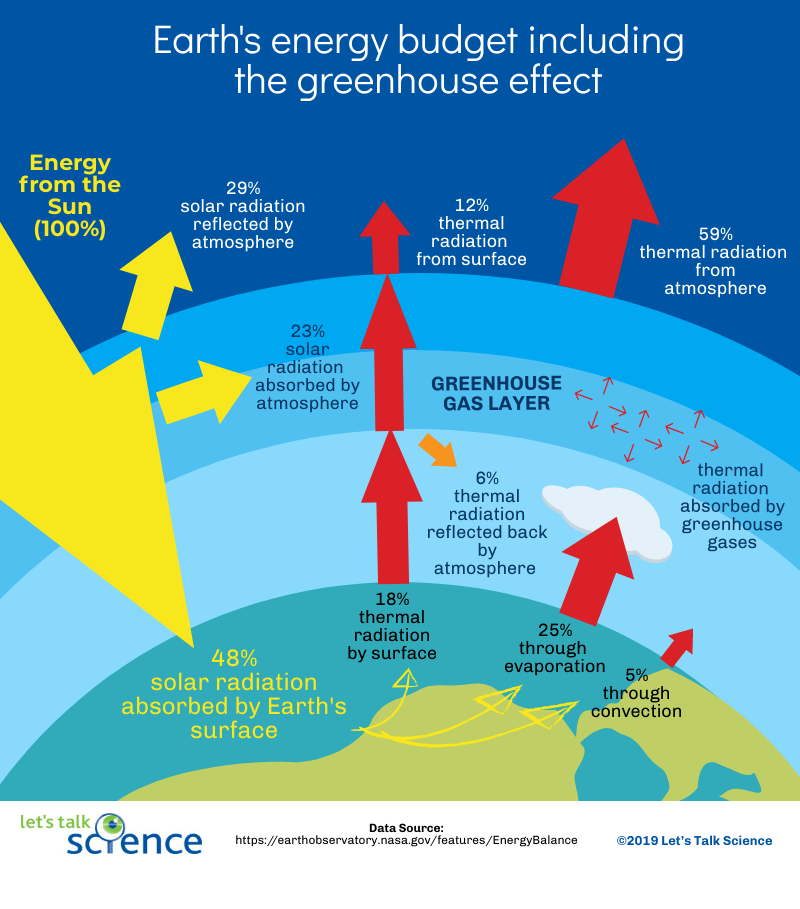



What Is Ocean Warming And Why Does It Matter Let S Talk Science
The cyclical nature of the greenhouse effect, which causes global warming Rachel Ignotofsky, Ten Speed Press Scientists measure global climate of The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist



Scott Denning Co2 The Greenhouse Effect Explained 10 Climate State




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor;The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as
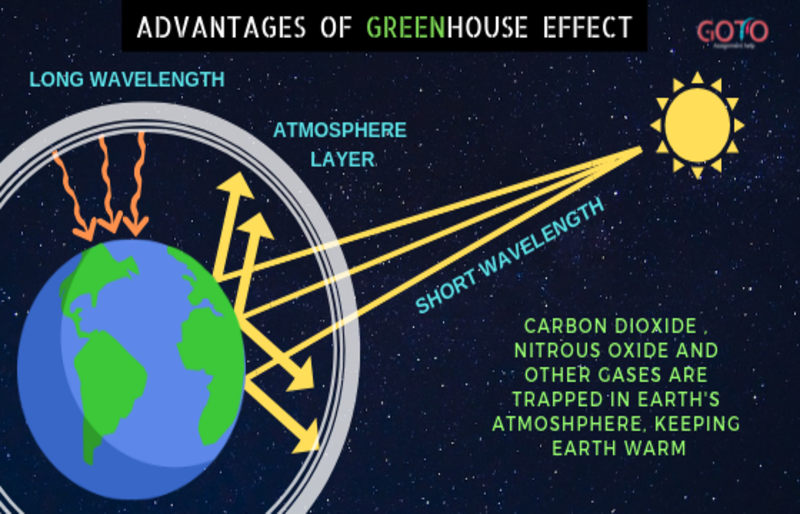



The Advantages Of Greenhouse Effect And The Role Of Greenhouse Gases



1
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on EarthA layer of gases in Earth's atmosphere naturally creates a greenhouse effect Without these gases in place, light and warmth from the sun would strike Earth, then largely reflect back into spaceWhile some don't believe that greenhouse gases caused by humans are the main culprit behind global warming, Bernstein showed graphs indicating otherwise The data, he explained, show pronounced increases in greenhouse gas levels in the United States during the Industrial Revolution of the late 1800s as well in the 1950s, when there was a




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Global Warming
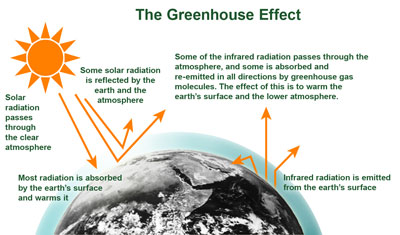
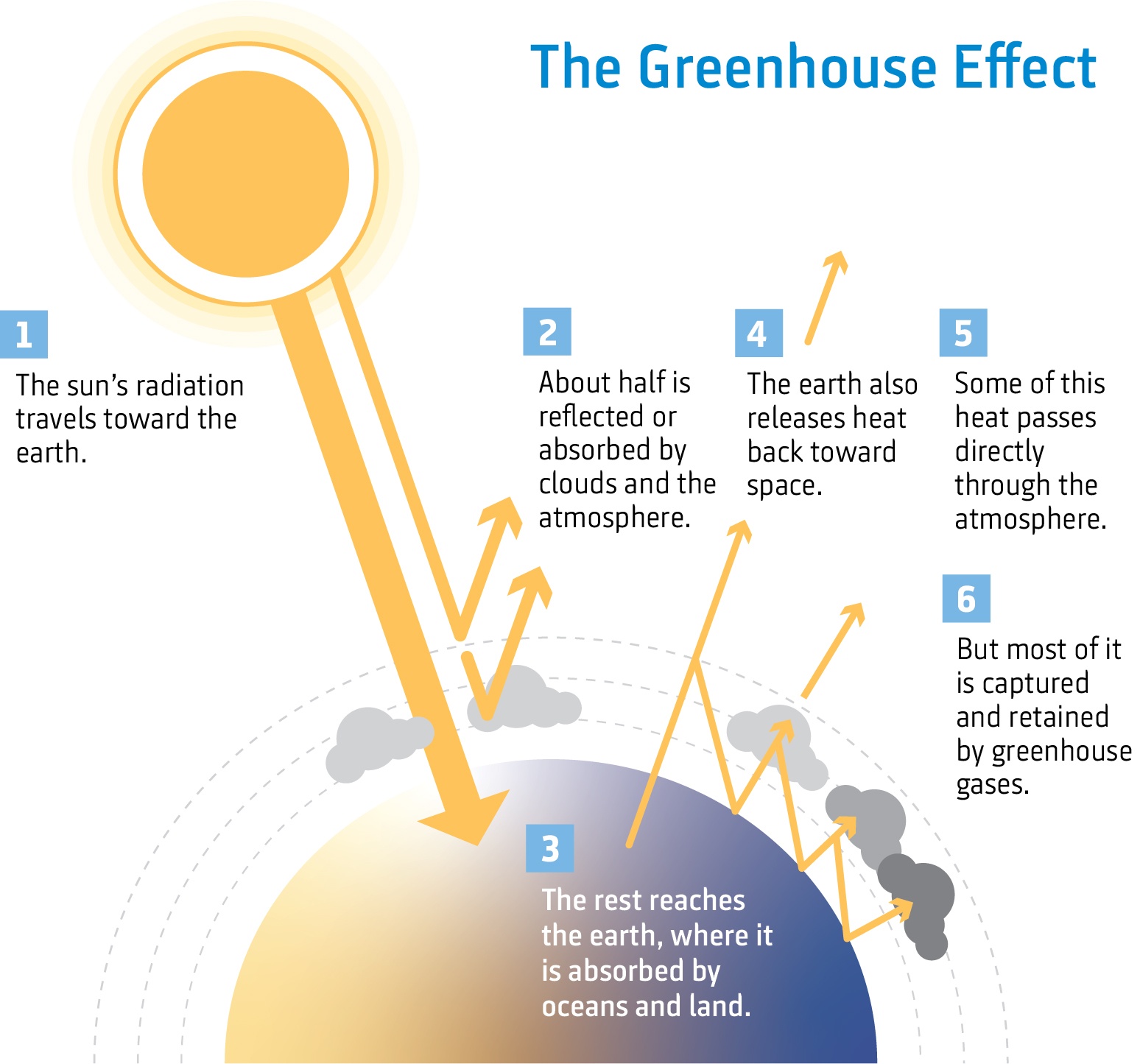
Greenhouse effect Step 1 Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere some of this is reflected back into space Step 2 The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth Step 3 Heat radiates from Earth towards space Step 4Absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the Earth's surface release infrared radiation in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm The diagram gives more details about this process,The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;




Social Posts




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube
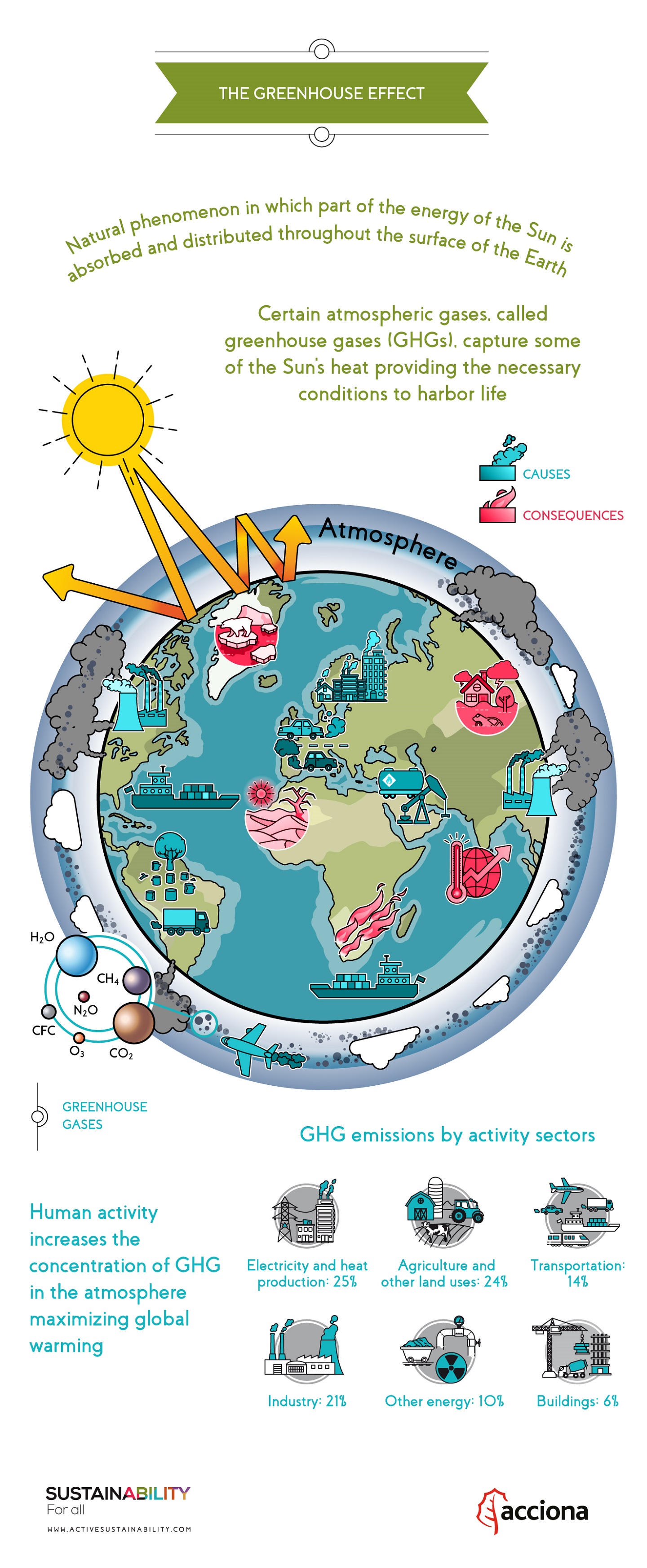



What Is The Greenhouse Effect
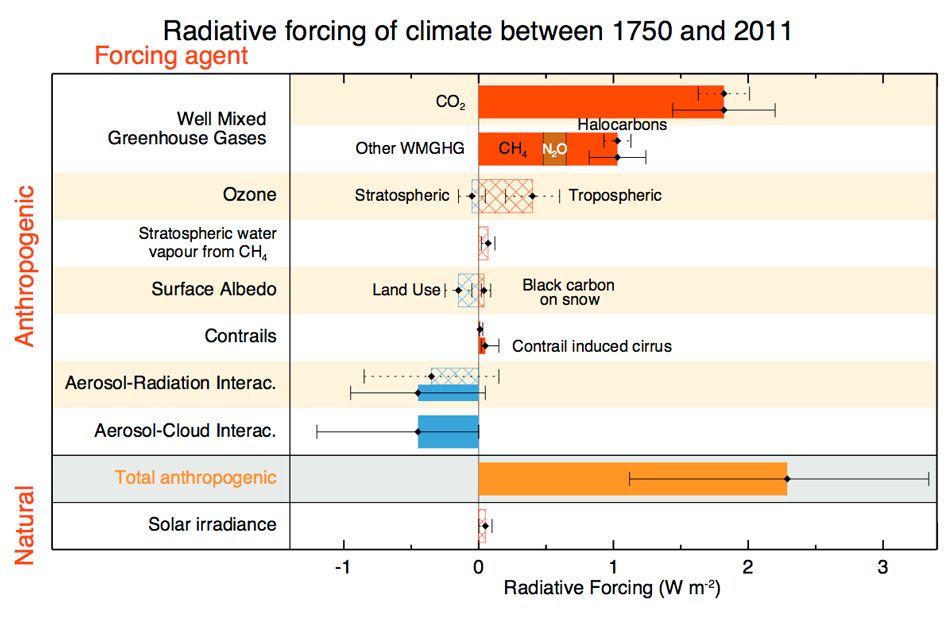



Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Climate Change Basics Ag Matters



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Environment For Kids Global Warming




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect Blog De Jose Felix Rodriguez Anton




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Experiment And Lesson For Kids



3




Ocean Warming Iucn



Greenhouse Gases



Untitled Document




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
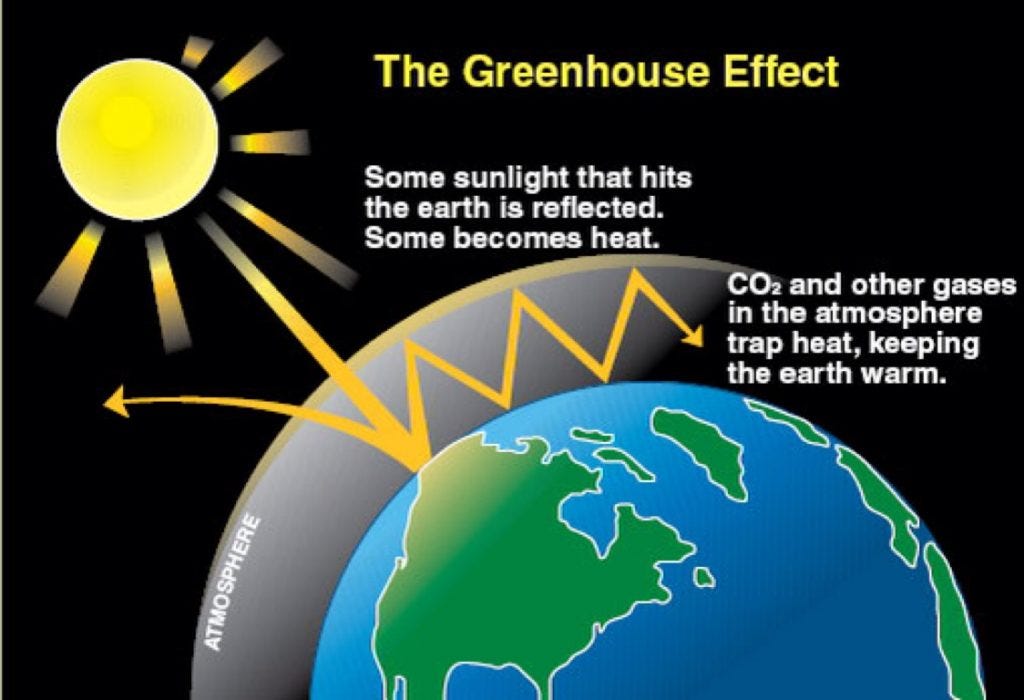



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Explaining The Greenhouse Effect Sustainability Youtube



The Effect Of Climate Change On Water Resources And Programs Watershed Academy Web Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Kids Corner




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Explained Animation Youtube



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service



Climate Change The Science Niwa




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect



Greenhouse Gases Science Learning Hub
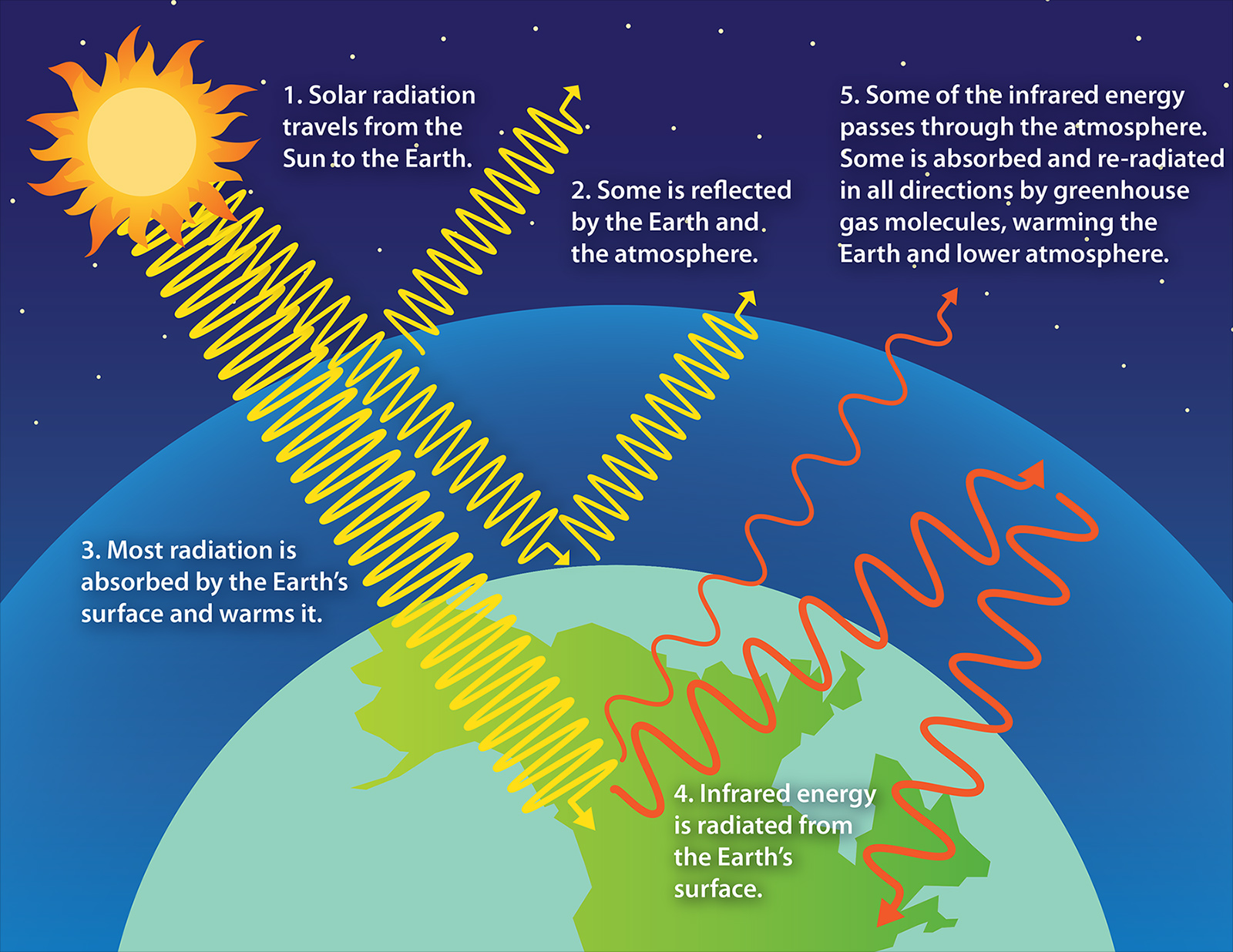



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




Science Vincent




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Climate Change Explained




Keeling Curve American Chemical Society




Climate Change Explained Just One Earth




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
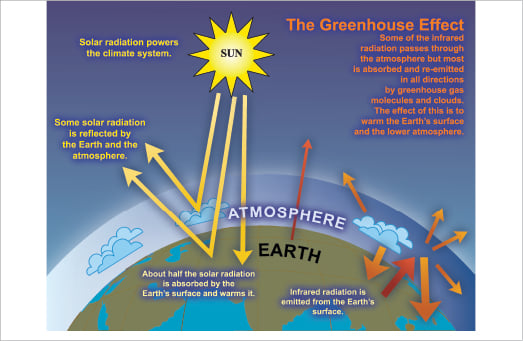



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
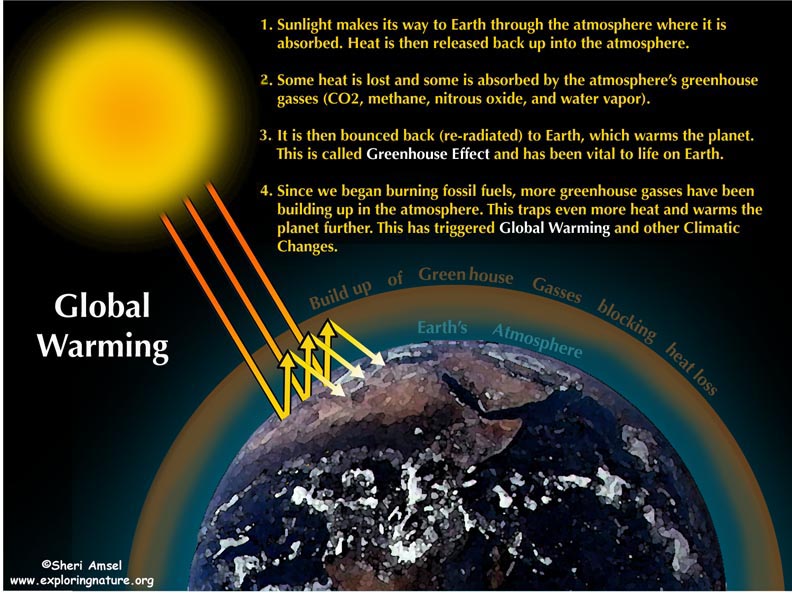



Global Warming Climate Change
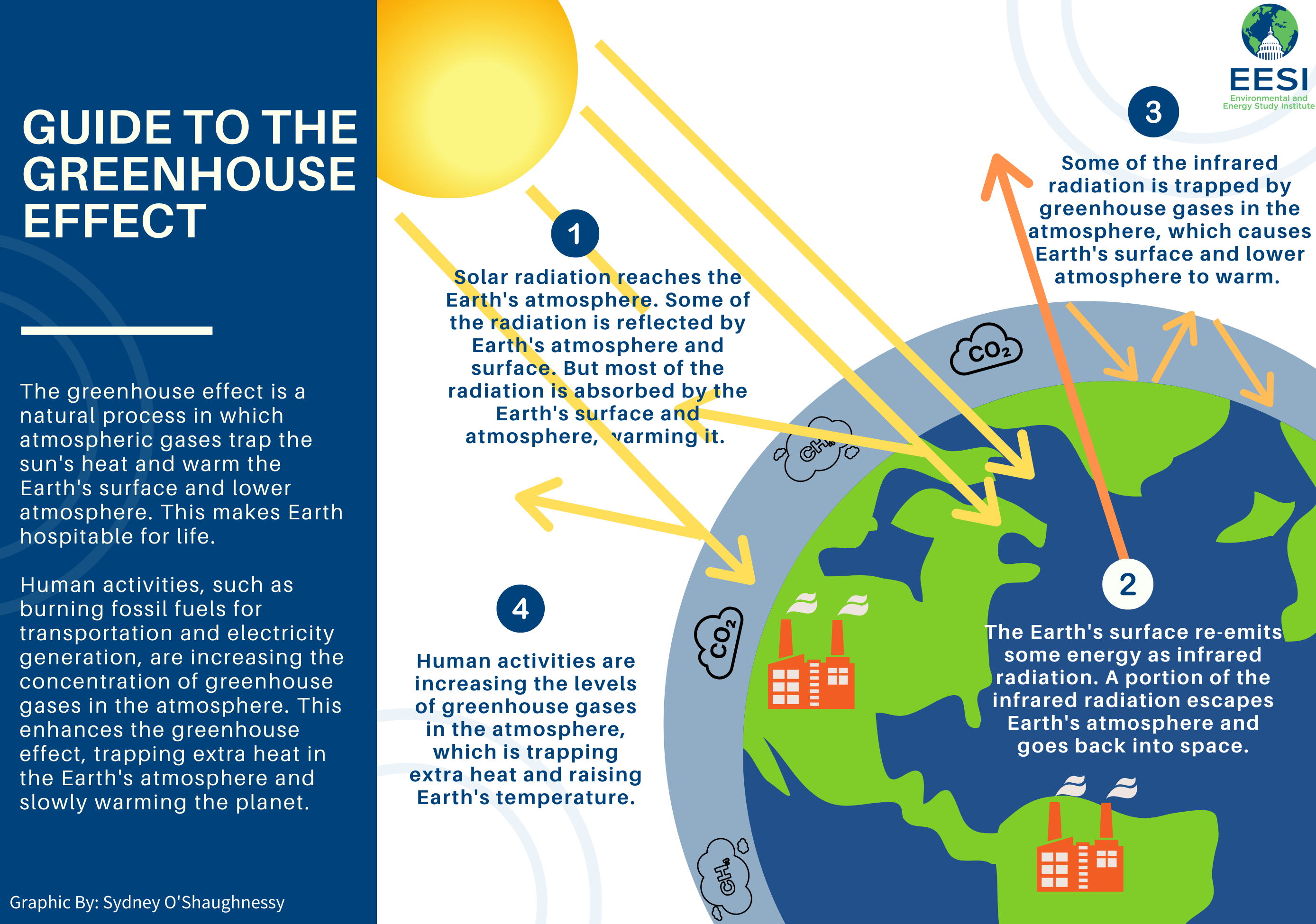



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Green House Gases Global Warming And Climate Change Public Health Notes




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Emmanuel Saenz Cause Effect
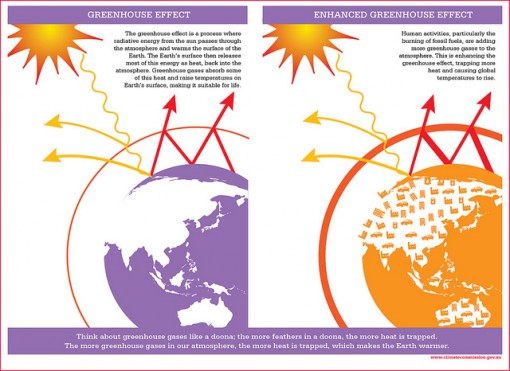



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today
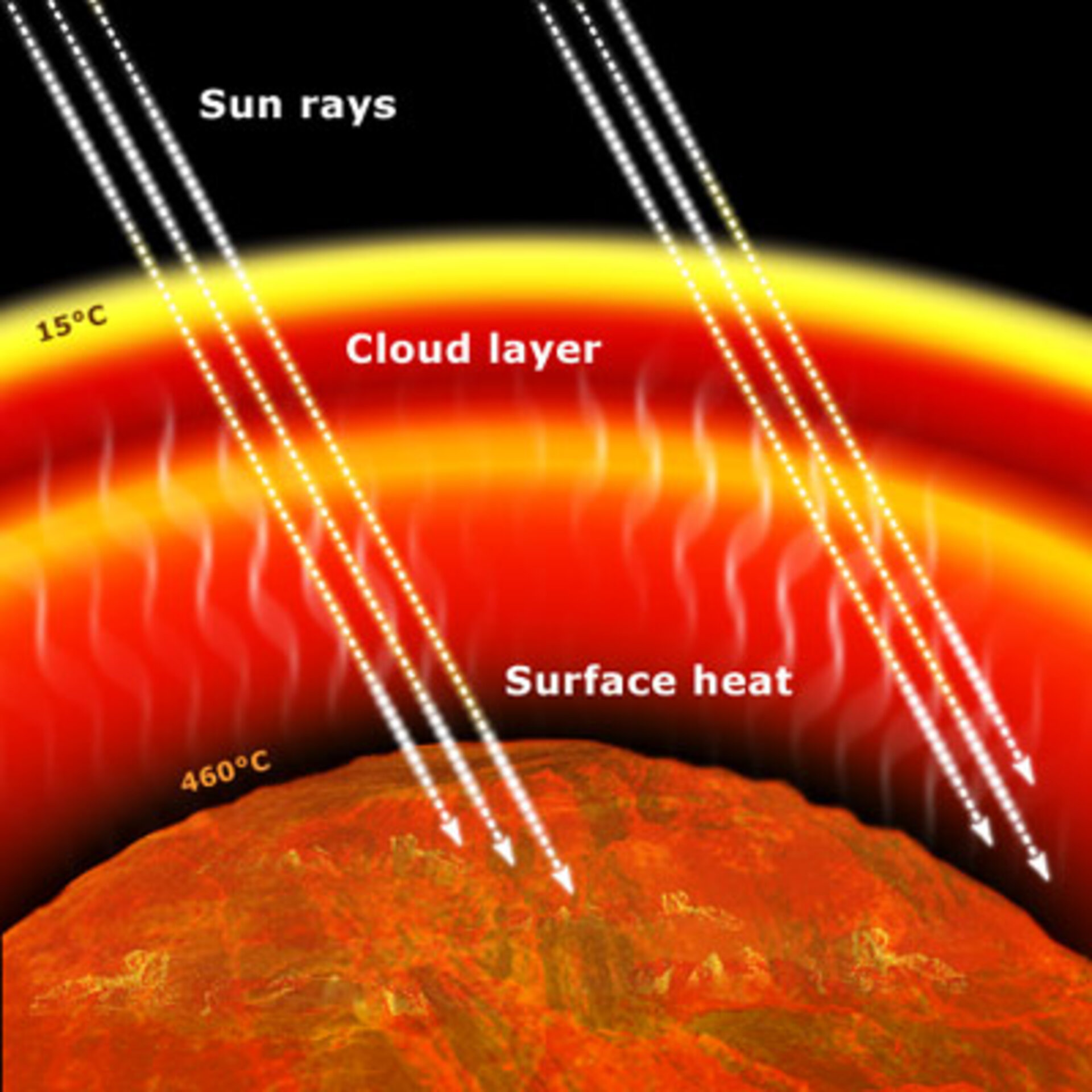



Esa Greenhouse Effects Also On Other Planets




What Is Greenhouse Effect Chemistry Questions
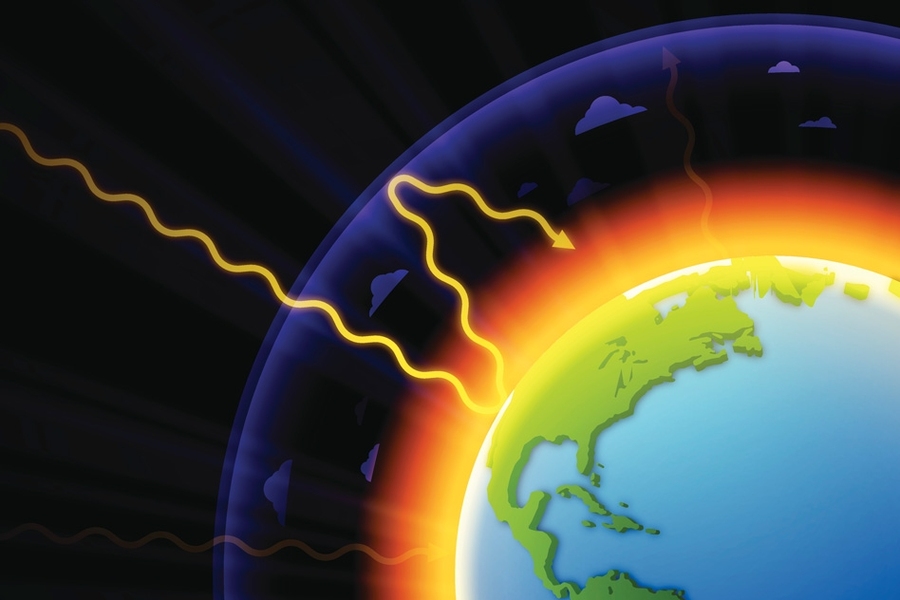




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




The Greenhouse Effect Artis Energy




Low Carbon Economies The Basics Explained News About Energy Storage Batteries Climate Change And The Environment
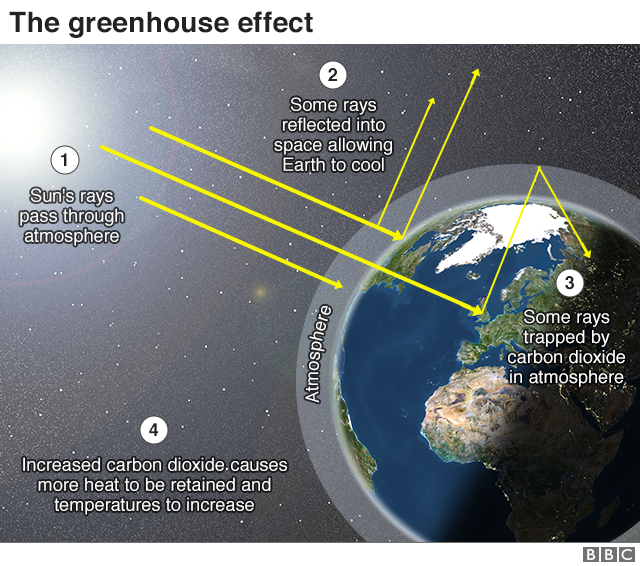



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News
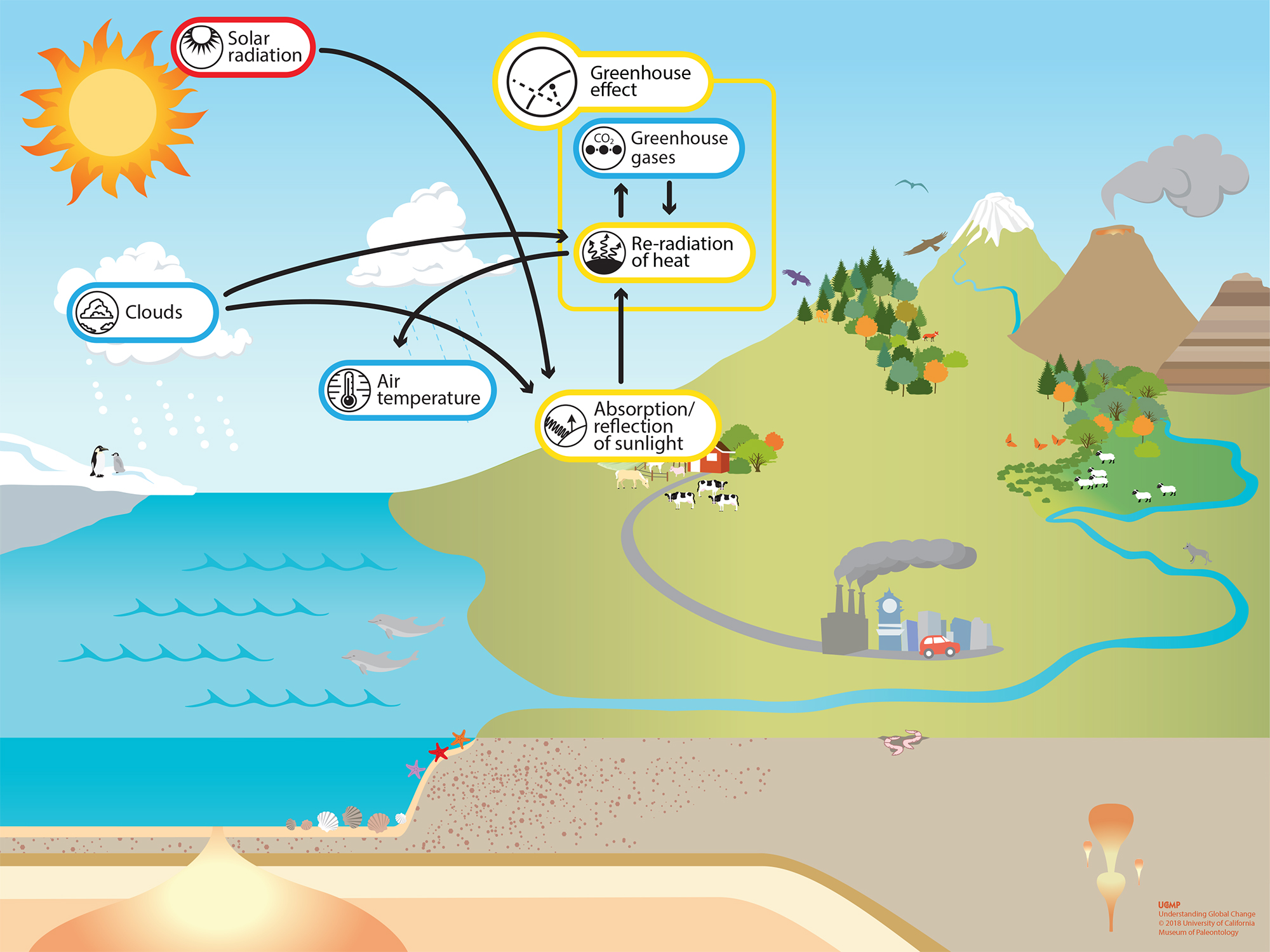



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education




Methane Climate Clean Air Coalition




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Effect Explained Edusaint Courses




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Kidminds




4 4 Climate Change Changes In Carbon Dioxide In Our Atmosphere In The Last 100 Years Why Has Carbon Dioxide Increased Carbon Dioxide Levels Ppm Ppt Download




The Greenhouse Effect World101




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment
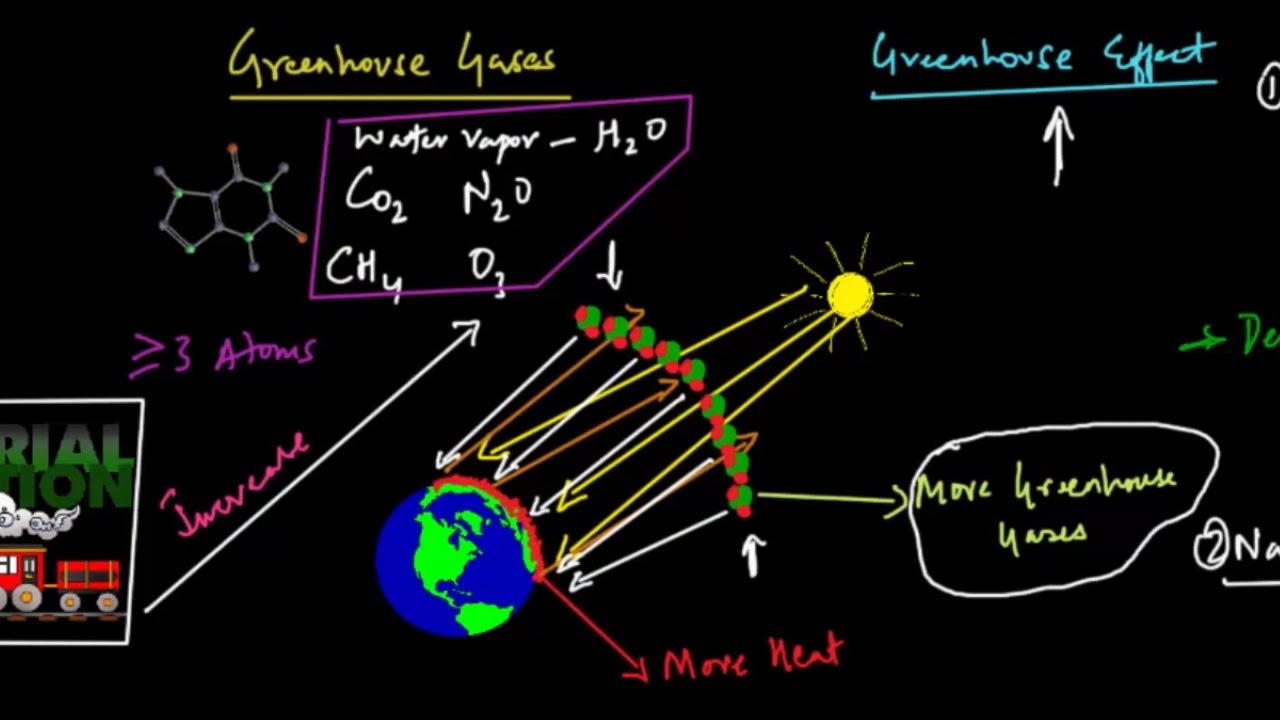



Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube
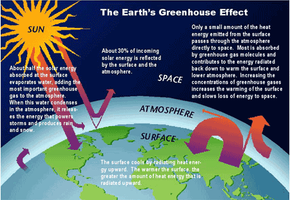



The Greenhouse Effect Howstuffworks




What Is The Greenhouse Effect The Environment For Kids Updated Version Youtube




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿